The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. There are 60 bones in each leg.

In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxa in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint on the outer (lateral) side of the pelvis.

The psoas major is a long fusiform muscle located in the lateral lumbar region between the vertebral column and the brim of the lesser pelvis. It joins the iliacus muscle to form the iliopsoas. In animals, this muscle is equivalent to the tenderloin.
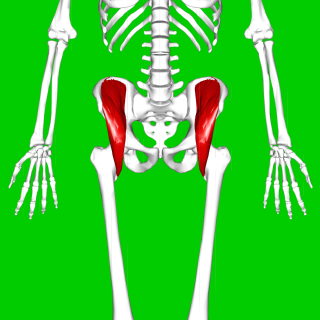
The iliacus is a flat, triangular muscle which fills the iliac fossa. It forms the lateral portion of iliopsoas, providing flexion of the thigh and lower limb at the acetabulofemoral joint.

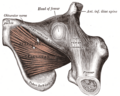
The quadratus femoris is a flat, quadrilateral skeletal muscle. Located on the posterior side of the hip joint, it is a strong external rotator and adductor of the thigh, but also acts to stabilize the femoral head in the acetabulum. The quadratus femoris is used in Meyer's muscle pedicle grafting to prevent avascular necrosis of femur head.

The iliopsoas muscle refers to the joined psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name iliopsoas. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest flexor of the hip.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.
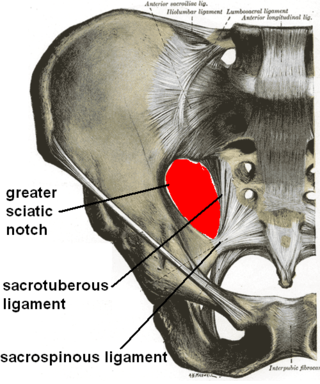
The sacrospinous ligament is a thin, triangular ligament in the human pelvis. The base of the ligament is attached to the outer edge of the sacrum and coccyx, and the tip of the ligament attaches to the spine of the ischium, a bony protuberance on the human pelvis. Its fibres are intermingled with the sacrotuberous ligament.

The medial meniscus is a fibrocartilage semicircular band that spans the knee joint medially, located between the medial condyle of the femur and the medial condyle of the tibia. It is also referred to as the internal semilunar fibrocartilage. The medial meniscus has more of a crescent shape while the lateral meniscus is more circular. The anterior aspects of both menisci are connected by the transverse ligament. It is a common site of injury, especially if the knee is twisted.
The ischial tuberosity, also known colloquially as the sit bones or sitz bones, or as a pair the sitting bones, is a large posterior bony protuberance on the superior ramus of the ischium. It marks the lateral boundary of the pelvic outlet.

The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet. Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.

The upper extremity, proximal extremity or superior epiphysis of the femur is the part of the femur closest to the pelvic bone and the trunk. It contains the following structures:

The wing(ala)of ilium is the large expanded portion of the ilium, the bone which bounds the greater pelvis laterally. It presents for examination two surfaces—an external and an internal—a crest, and two borders—an anterior and a posterior.

The anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS) is a bony eminence on the anterior border of the hip bone, or, more precisely, the wing of the ilium.

The crest of the ilium is the superior border of the wing of ilium and the superiolateral margin of the greater pelvis.

The intertrochanteric line is a line upon the anterior aspect of the proximal end of the femur, extending between the lesser trochanter and the greater trochanter. It is a rough, variable ridge.

The articular capsule of the knee joint is the wide and lax joint capsule of the knee. It is thin in front and at the side, and contains the patella, ligaments, menisci, and bursae of the knee. The capsule consists of an inner synovial membrane, and an outer fibrous membrane separated by fatty deposits anteriorly and posteriorly.

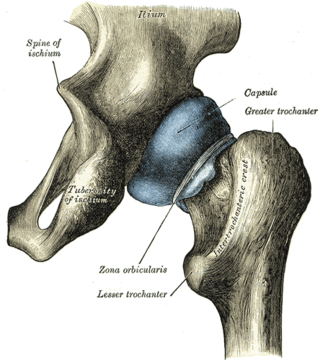
The capsule of hip joint, articular capsule, or capsular ligament is strong and dense attachment of the hip joint.

The hip bone is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis.

The pelvis is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.