This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(June 2015) |
| Lateral meniscus | |
|---|---|
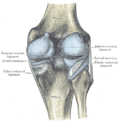
 Knee from the side, with lateral meniscus simply labeled as "meniscus". | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | meniscus lateralis |
| TA98 | A03.6.08.002 |
| TA2 | 1885 |
| FMA | 44631 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
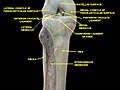
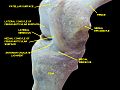
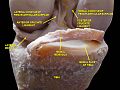
The lateral meniscus (external semilunar fibrocartilage) is a fibrocartilaginous band that spans the lateral side of the interior of the knee joint. It is one of two menisci of the knee, the other being the medial meniscus. It is nearly circular and covers a larger portion of the articular surface than the medial. It can occasionally be injured or torn by twisting the knee or applying direct force, as seen in contact sports.