
In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.

In anatomy, the axis is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests. The spinal cord passes through the axis.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. The radius is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.

The inguinal ligament, also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop.

In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxa in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint on the outer (lateral) side of the pelvis.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.

In human anatomy, the subtalar joint, also known as the talocalcaneal joint, is a joint of the foot. It occurs at the meeting point of the talus and the calcaneus.

The lateral meniscus is a fibrocartilaginous band that spans the lateral side of the interior of the knee joint. It is one of two menisci of the knee, the other being the medial meniscus. It is nearly circular and covers a larger portion of the articular surface than the medial. It can occasionally be injured or torn by twisting the knee or applying direct force, as seen in contact sports.

The calcaneofibular ligament is a narrow, rounded cord, running from the tip of the lateral malleolus of the fibula downward and slightly backward to a tubercle on the lateral surface of the calcaneus. It is part of the lateral collateral ligament, which opposes the hyperinversion of the subtalar joint, as in a common type of ankle sprain.
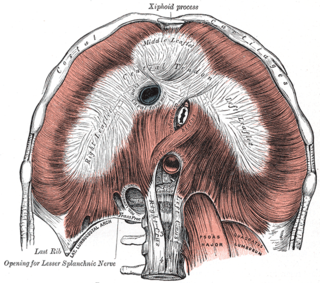
The lateral arcuate ligament is a ligament under the diaphragm that arches across the upper part of the quadratus lumborum muscle. It is traversed by the subcostal nerve, artery and vein.

The lateral umbilical fold is an elevation of the peritoneum lining the inner/posterior surface of the lower anterior abdominal wall formed by the underlying inferior epigastric artery and inferior epigastric vein which the peritoneum covers. Superiorly, the lateral umbilical fold ends where the vessels reach and enter the rectus sheath at the arcuate line of rectus sheath; in spite of the name, the lateral umbilical folds do not extend as far superiorly as the umbilicus. Inferiorly, it extends to just medial to the deep inguinal ring.
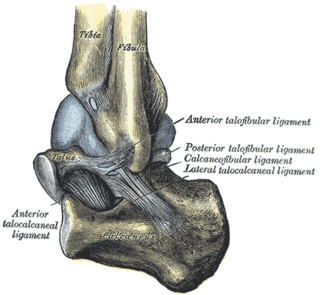
The inferior tibiofibular joint, also known as the distal tibiofibular joint, is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the distal end of the fibula, and a rough concave surface on the lateral side of the tibia.

The sacrococcygeal symphysis is an amphiarthrodial joint, formed between the oval surface at the apex of the sacrum, and the base of the coccyx.

The talocalcaneonavicular joint is a ball and socket joint in the foot; the rounded head of the talus is received into the concavity formed by the posterior surface of the navicular, the anterior articular surface of the calcaneus, and the upper surface of the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament.

The medial umbilical ligament, cord of umbilical artery, or obliterated umbilical artery is a paired structure found in human anatomy. It is on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall, and is covered by the medial umbilical folds. It is different from the median umbilical ligament, a structure that represents the remnant of the embryonic urachus.

A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.
The anterior meniscofemoral ligament is a small fibrous band of the knee joint. It arises from the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus and passes superiorly and medially in front of the posterior cruciate ligament to attach to the lateral surface of medial condyle of the femur.


















