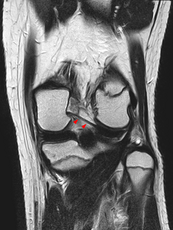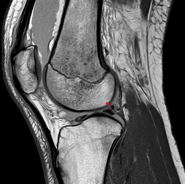
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a ligament in each knee of humans and various other animals. It works as a counterpart to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). It connects the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia to the medial condyle of the femur. This configuration allows the PCL to resist forces pushing the tibia posteriorly relative to the femur.

The Segond fracture is a type of avulsion fracture from the lateral tibial plateau of the knee, immediately below the articular surface of the tibia.

The popliteus muscle in the leg is used for unlocking the knees when walking, by laterally rotating the femur on the tibia during the closed chain portion of the gait cycle. In open chain movements, the popliteus muscle medially rotates the tibia on the femur. It is also used when sitting down and standing up. It is the only muscle in the posterior (back) compartment of the lower leg that acts just on the knee and not on the ankle. The gastrocnemius muscle acts on both joints.

The medial meniscus is a fibrocartilage semicircular band that spans the knee joint medially, located between the medial condyle of the femur and the medial condyle of the tibia. It is also referred to as the internal semilunar fibrocartilage. The medial meniscus has more of a crescent shape while the lateral meniscus is more circular. The anterior aspects of both menisci are connected by the transverse ligament. It is a common site of injury, especially if the knee is twisted.

The lateral meniscus is a fibrocartilaginous band that spans the lateral side of the interior of the knee joint. It is one of two menisci of the knee, the other being the medial meniscus. It is nearly circular and covers a larger portion of the articular surface than the medial. It can occasionally be injured or torn by twisting the knee or applying direct force, as seen in contact sports.
The knee examination, in medicine and physiotherapy, is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with knee pain or a history that suggests a pathology of the knee joint.

The stifle joint is a complex joint in the hind limbs of quadruped mammals such as the sheep, horse or dog. It is the equivalent of the human knee and is often the largest synovial joint in the animal's body. The stifle joint joins three bones: the femur, patella, and tibia. The joint consists of three smaller ones: the femoropatellar joint, medial femorotibial joint, and lateral femorotibial joint.
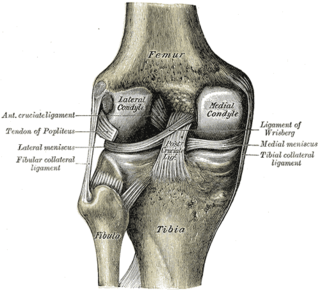
The lower extremity of femur is the lower end of the femur in human and other animals, closer to the knee. It is larger than the upper extremity of femur, is somewhat cuboid in form, but its transverse diameter is greater than its antero-posterior; it consists of two oblong eminences known as the lateral condyle and medial condyle.

The unhappy triad, also known as a blown knee among other names, is an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and meniscus. Analysis during the 1990s indicated that this 'classic' O'Donoghue triad is actually an unusual clinical entity among athletes with knee injuries. Some authors mistakenly believe that in this type of injury, "combined anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligament disruptions that were incurred during athletic endeavors" always present with concomitant medial meniscus injury. However, the 1990 analysis showed that lateral meniscus tears are more common than medial meniscus tears in conjunction with sprains of the ACL.

The articular capsule of the knee joint is the wide and lax joint capsule of the knee. It is thin in front and at the side, and contains the patella, ligaments, menisci, and bursae of the knee. The capsule consists of an inner synovial membrane, and an outer fibrous membrane separated by fatty deposits anteriorly and posteriorly.

The coronary ligaments of the knee are portions of the joint capsule which connect the inferior edges of the fibrocartilaginous menisci to the periphery of the tibial plateaus.
The anterior meniscofemoral ligament is a small fibrous band of the knee joint. It arises from the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus and passes superiorly and medially in front of the posterior cruciate ligament to attach to the lateral surface of medial condyle of the femur.

A tear of a meniscus is a rupturing of one or more of the fibrocartilage strips in the knee called menisci. When doctors and patients refer to "torn cartilage" in the knee, they actually may be referring to an injury to a meniscus at the top of one of the tibiae. Menisci can be torn during innocuous activities such as walking or squatting. They can also be torn by traumatic force encountered in sports or other forms of physical exertion. The traumatic action is most often a twisting movement at the knee while the leg is bent. In older adults, the meniscus can be damaged following prolonged 'wear and tear'. Especially acute injuries can lead to displaced tears which can cause mechanical symptoms such as clicking, catching, or locking during motion of the joint. The joint will be in pain when in use, but when there is no load, the pain goes away.

The transverse or (anterior) meniscomeniscal ligament is a ligament in the knee joint that connects the anterior convex margin of the lateral meniscus to the anterior end of the medial meniscus.

Discoid meniscus is a rare human anatomic variant that usually affects the lateral meniscus of the knee. Usually a person with this anomaly has no complaints; however, it may present as pain, swelling, or a snapping sound heard from the affected knee. Strong suggestive findings on magnetic resonance imaging includes a thickened meniscal body seen on more than two contiguous sagittal slices.
Posterolateral corner injuries of the knee are injuries to a complex area formed by the interaction of multiple structures. Injuries to the posterolateral corner can be debilitating to the person and require recognition and treatment to avoid long term consequences. Injuries to the PLC often occur in combination with other ligamentous injuries to the knee; most commonly the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). As with any injury, an understanding of the anatomy and functional interactions of the posterolateral corner is important to diagnosing and treating the injury.

Medial knee injuries are the most common type of knee injury. The medial ligament complex of the knee consists of:

The intercondylar area is the separation between the medial and lateral condyle on the upper extremity of the tibia. The anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments and the menisci attach to the intercondylar area.