
The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula.

The heel is the prominence at the posterior end of the foot. It is based on the projection of one bone, the calcaneus or heel bone, behind the articulation of the bones of the lower leg.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.

In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.

The metatarsal bones or metatarsus are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones and the phalanges (toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side : the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal. The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. A bovine hind leg has two metatarsals.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei of the foot are four muscles situated between the metatarsal bones.
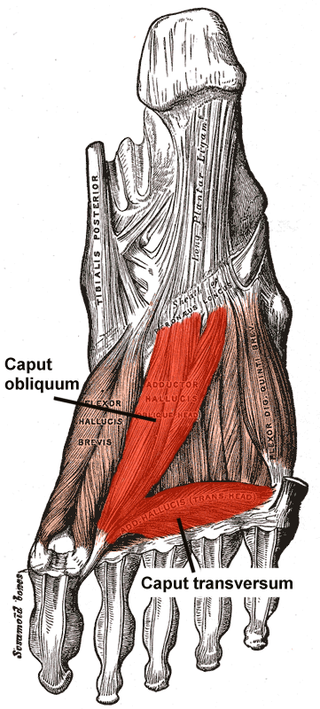
The Adductor hallucis arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve.
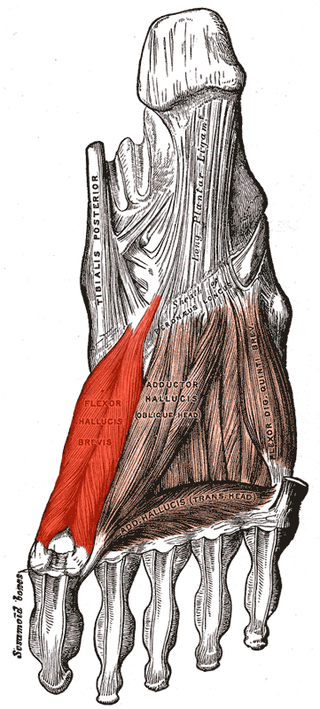
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a muscle of the foot that flexes the big toe.

In human anatomy, plantar interossei muscles are three muscles located between the metatarsal bones in the foot.
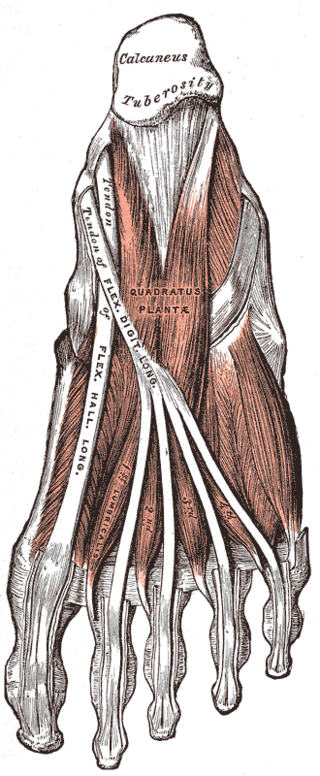
The quadratus plantae is separated from the muscles of the first layer by the lateral plantar vessels and nerve. It acts to aid in flexing the 2nd to 5th toes and is one of the few muscles in the foot with no homolog in the hand.
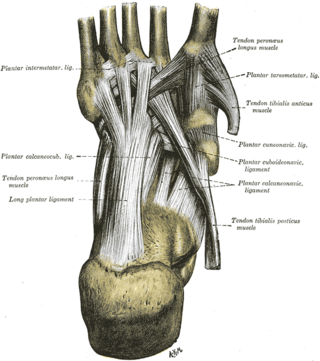
The long plantar ligament is a long ligament on the underside of the foot that connects the calcaneus with the 2nd to 5th metatarsal.

The plantar calcaneocuboid ligament is a ligament on the bottom of the foot that connects the calcaneus to the cuboid bone. It lies deep to the long plantar ligament.

The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament is a complex of three ligaments on the underside of the foot that connect the calcaneus with the navicular bone.

The intermetatarsal joints are the articulations between the base of metatarsal bones.

The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand.

The fourth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is smaller in size than the third metatarsal bone and is the third longest of the five metatarsal bones. The fourth metatarsal is analogous to the fourth metacarpal bone in the hand

The first metatarsal bone is the bone in the foot just behind the big toe. The first metatarsal bone is the shortest of the metatarsal bones and by far the thickest and strongest of them.
The plantar cuboideonavicular ligament is a fibrous band that connects the plantar surfaces of the cuboid and navicular bones.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
















