This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

A plantar wart is a wart occurring on the bottom of the foot or toes. Their color is typically similar to that of the skin. Small black dots often occur on the surface. One or more may occur in an area. They may result in pain with pressure such that walking is difficult.
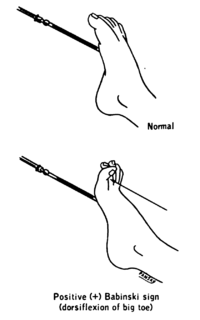
The plantar reflex is a reflex elicited when the sole of the foot is stimulated with a blunt instrument. The reflex can take one of two forms. In normal adults, the plantar reflex causes a downward response of the hallux (flexion). An upward response (extension) of the hallux is known as the Babinski response or Babinski sign, named after the neurologist Joseph Babinski. The presence of the Babinski sign can identify disease of the spinal cord and brain in adults, and also exists as a primitive reflex in infants.
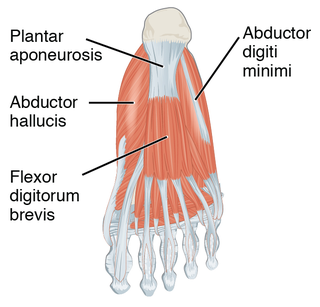
The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom of the foot. It runs from the tuberosity of the calcaneus forward to the heads of the metatarsal bones.

Plantar fasciitis is a disorder of the connective tissue which supports the arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and bottom of the foot that is usually most severe with the first steps of the day or following a period of rest. Pain is also frequently brought on by bending the foot and toes up towards the shin. The pain typically comes on gradually, and it affects both feet in about one third of cases.

The tibialis posterior is the most central of all the leg muscles, and is located in the deep posterior compartment of the leg.

Plantar fascial fibromatosis, also known as Ledderhose's disease, Morbus Ledderhose, and plantar fibromatosis, is a relatively uncommon non-malignant thickening of the feet's deep connective tissue, or fascia. In the beginning, where nodules start growing in the fascia of the foot the disease is minor. Over time walking becomes painful. The disease is named after Dr. Georg Ledderhose, a German surgeon who described the condition for the first time in 1894. A similar disease is Dupuytren's disease, which affects the hand and causes bent hand or fingers.

In human anatomy, plantar interossei muscles are three muscles located between the metatarsal bones in the foot.

A calcaneal spur is a bony outgrowth from the calcaneal tuberosity. Calcaneal spurs are typically detected by x-ray examination. It is a form of exostosis.
The sole is the bottom of the foot.
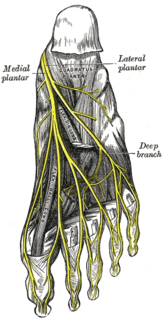
The medial plantar nerve is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve, which accompanies the medial plantar artery.
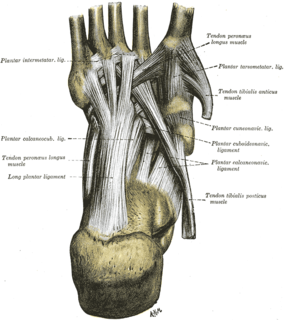
The long plantar ligament is a long ligament on the underside of the foot that connects the calcaneus with the cuboid bone.

The lateral plantar artery, much larger than the medial, passes obliquely lateralward and forward to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone.

The plantar metatarsal arteries are four in number, arising from the convexity of the plantar arch. They run forward between the metatarsal bones and in contact with the Interossei. They are located in the fourth layer of the foot.

The plantar calcaneocuboid ligament is a ligament on the bottom of the foot that connects the calcaneus to the cuboid bone. It lies deep to the long plantar ligament.

The plantar arch is a circulatory anastomosis formed from:

The tarsal tunnel is found along the inner leg posterior to the medial malleolus.

The superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into a proper and a common plantar digital nerve:
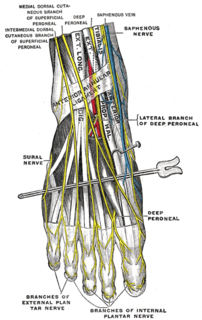
The proper plantar digital nerves of lateral plantar nerve are nerves of the foot that arise from the superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve. The superficial branch splits into a proper digital nerve and a common digital nerve:

The proper plantar digital nerves of medial plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. They primarily arise from the medial plantar nerve's superficial and deep branches. The superficial branch of the medial plantar nerve turns into a proper digital nerve and is responsible for supplies the medial side of the great toe.

The common plantar digital arteries are arteries of the foot.












