
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.
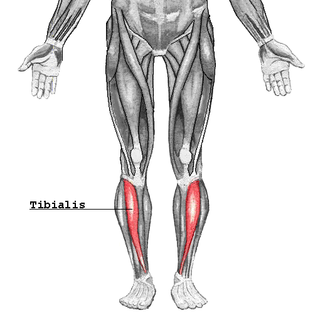
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the upper portion of the tibia; it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.
Splints is an ailment of the horse or pony, characterized by a hard, bony swelling, usually on the inside of a front leg, lying between the splint and cannon bone or on the splint bone itself. It may be "hot," meaning that it occurred recently and is still painful; or "cold," meaning that the splint has completely recovered and there is no longer any swelling or pain associated with it. Bucked shins are sometimes called 'shin splints,' which involve small stress fractures of the dorsal cannon bone, often seen in race training, and discussed elsewhere.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei of the foot are four muscles situated between the metatarsal bones.
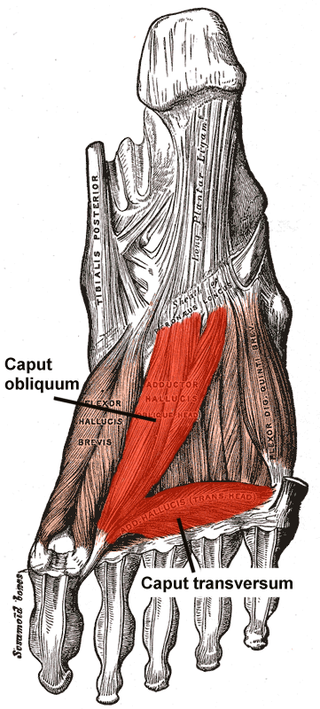
The Adductor hallucis arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

The palmar aponeurosis invests the muscles of the palm, and consists of central, lateral, and medial portions.

The arches of the foot, formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, strengthened by ligaments and tendons, allow the foot to support the weight of the body in the erect posture with the least weight.
A Interosseous ligament can refer to:
The transverse metatarsal ligament is a narrow band which runs across and connects together the heads of all the metatarsal bones. It is blended anteriorly with the plantar (glenoid) ligaments of the metatarsophalangeal articulations.
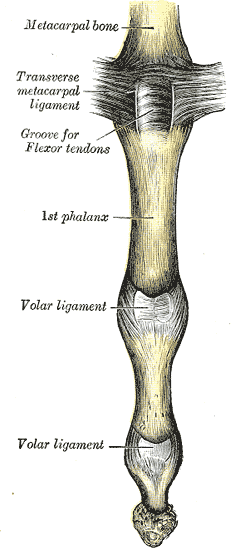
The deep transverse metacarpal ligament connects the palmar surfaces of metacarpophalangeal joints of all the fingers of the hand except the thumb.
The intermetacarpal joints are in the hand formed between the metacarpal bones. The bases of the second, third, fourth and fifth metacarpal bones articulate with one another by small surfaces covered with cartilage. The metacarpal bones are connected together by dorsal, palmar, and interosseous ligaments.

The tarsometatarsal joints are arthrodial joints in the foot. The tarsometatarsal joints involve the first, second and third cuneiform bones, the cuboid bone and the metatarsal bones. The eponym of Lisfranc joint is 18th–19th-century surgeon and gynecologist Jacques Lisfranc de St. Martin.
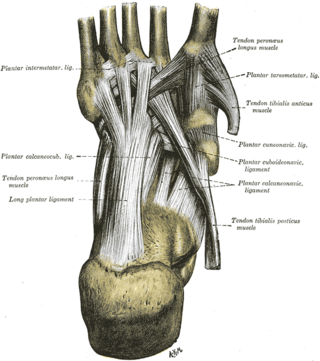
The intermetatarsal joints are the articulations between the base of metatarsal bones.
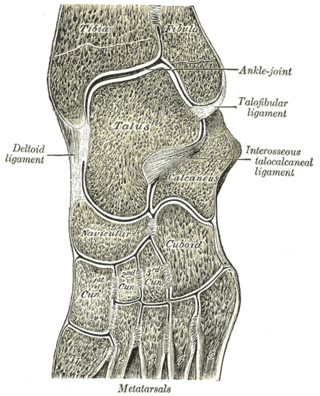
The intercuneiform joints are the joints the cuneiform bones.

The intercarpal joints can be subdivided into three sets of joints : Those of the proximal row of carpal bones, those of the distal row of carpal bones, and those of the two rows with each other.

The Lisfranc ligament is one of several ligaments which connects the medial cuneiform bone to the second metatarsal. Sometimes, the term Lisfranc ligament refers specifically to the ligament that connects the superior, lateral surface of the medial cuneiform to the superior, medial surface of the base of the second metatarsal.
The interosseous cuneometatarsal ligaments are fibrous bands that connect the adjacent surfaces of the cuneiform and the metatarsal bones.

The interosseous metatarsal ligaments are ligaments in the foot.
Metatarsal ligaments may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.












