The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.

In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.
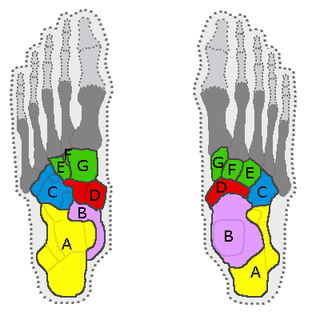
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot and hindfoot.
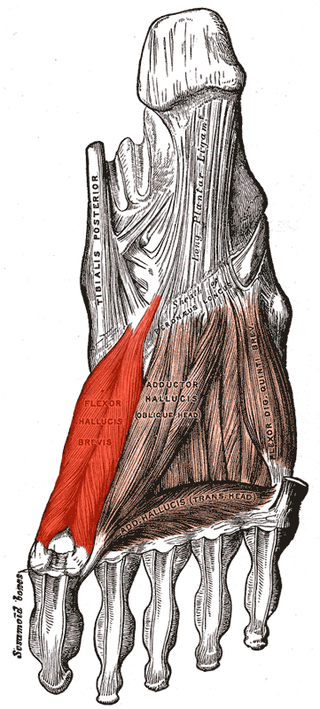
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a muscle of the foot that flexes the big toe.
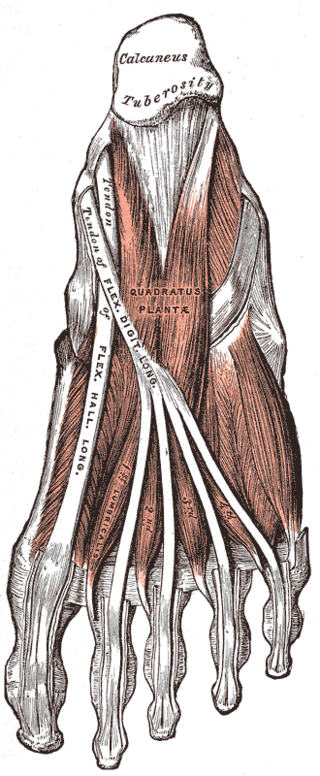
The quadratus plantae is separated from the muscles of the first layer by the lateral plantar vessels and nerve. It acts to aid in flexing the 2nd to 5th toes and is one of the few muscles in the foot with no homolog in the hand.

In human anatomy, the subtalar joint, also known as the talocalcaneal joint, is a joint of the foot. It occurs at the meeting point of the talus and the calcaneus.
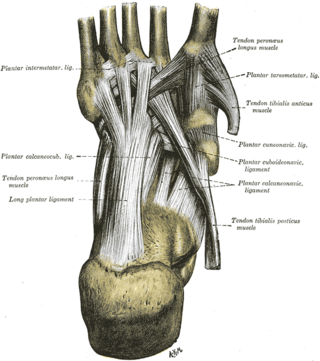
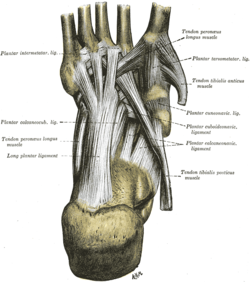
The long plantar ligament is a long ligament on the underside of the foot that connects the calcaneus with the 2nd to 5th metatarsal.

The arches of the foot, formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, strengthened by ligaments and tendons, allow the foot to support the weight of the body in the erect posture with the least weight.

The talocalcaneonavicular joint is a ball and socket joint in the foot; the rounded head of the talus is received into the concavity formed by the posterior surface of the navicular, the anterior articular surface of the calcaneus, and the upper surface of the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament.

The calcaneocuboid joint is the joint between the calcaneus and the cuboid bone.

The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament is a complex of three ligaments on the underside of the foot that connect the calcaneus with the navicular bone.

The bifurcated ligament is a strong band, attached behind to the deep hollow on the upper surface of the calcaneus and dividing in front in a Y-shaped manner into a calcaneocuboid and a calcaneonavicular part.

The tarsometatarsal joints are arthrodial joints in the foot. The tarsometatarsal joints involve the first, second and third cuneiform bones, the cuboid bone and the metatarsal bones. The eponym of Lisfranc joint is 18th–19th-century surgeon and gynecologist Jacques Lisfranc de St. Martin.

The dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament is a thin but broad fasciculus, which passes between the contiguous surfaces of the calcaneus and cuboid, on the dorsal surface of the joint.

The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand.
The calcaneocuboid ligament is a fibrous band that connects the superior surface of the calcaneus to the dorsal surface of the cuboid bone.

Cuboid syndrome or cuboid subluxation describes a condition that results from subtle injury to the calcaneocuboid joint, and ligaments in the vicinity of the cuboid bone, one of seven tarsal bones of the human foot.
Plantar ligament refer to ligaments in the sole of the foot: