
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.
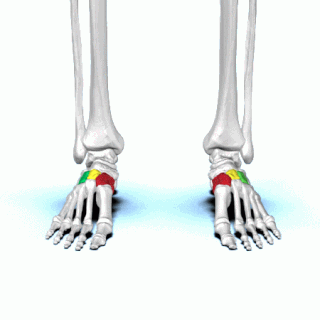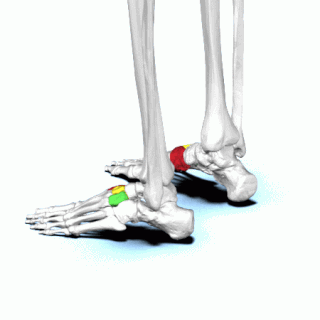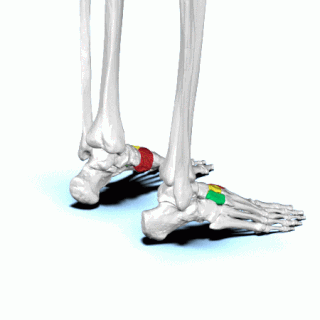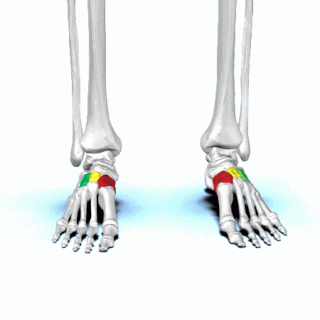
There are three cuneiform ("wedge-shaped") bones in the human foot:

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.

The flexor digitorum longus muscle is situated on the tibial side of the leg. At its origin it is thin and pointed, but it gradually increases in size as it descends. It serves to flex the second, third, fourth, and fifth toes.

In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.
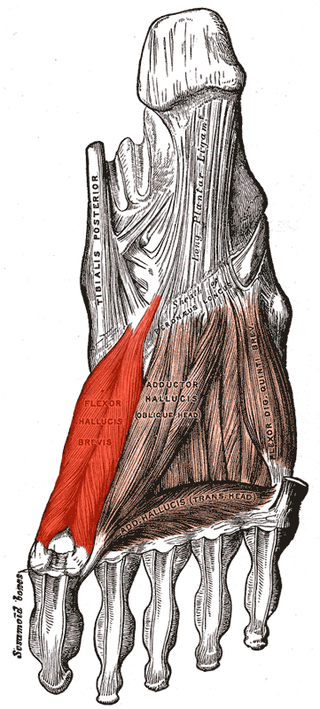
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a muscle of the foot that flexes the big toe.
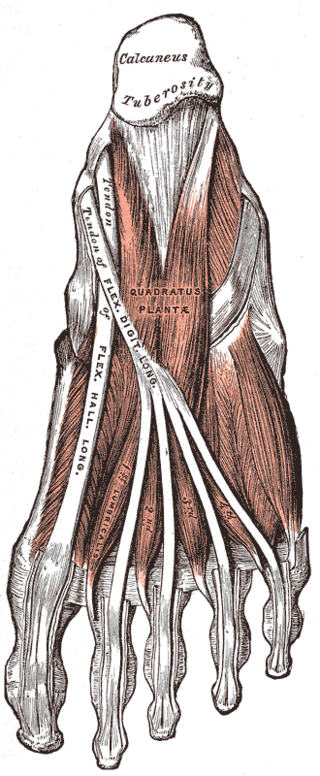
The quadratus plantae is separated from the muscles of the first layer by the lateral plantar vessels and nerve. It acts to aid in flexing the 2nd to 5th toes and is one of the few muscles in the foot with no homolog in the hand.

The inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot is a Y-shaped band placed in front of the ankle-joint, the stem of the Y being attached laterally to the upper surface of the calcaneus, in front of the depression for the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament; it is directed medialward as a double layer, one lamina passing in front of, and the other behind, the tendons of the peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus.

The arches of the foot, formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, strengthened by ligaments and tendons, allow the foot to support the weight of the body in the erect posture with the least weight.
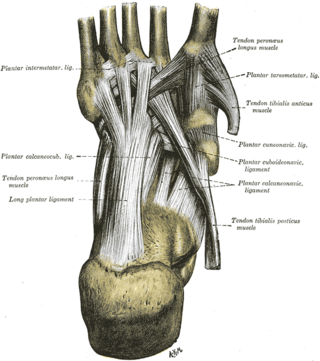
The plantar calcaneocuboid ligament is a ligament on the bottom of the foot that connects the calcaneus to the cuboid bone. It lies deep to the long plantar ligament.

A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.

The fourth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is smaller in size than the third metatarsal bone and is the third longest of the five metatarsal bones. The fourth metatarsal is analogous to the fourth metacarpal bone in the hand

The first metatarsal bone is the bone in the foot just behind the big toe. The first metatarsal bone is the shortest of the metatarsal bones and by far the thickest and strongest of them.

The deep fascia of leg, or crural fascia forms a complete investment to the muscles, and is fused with the periosteum over the subcutaneous surfaces of the bones.



















