| Upper extremity of femur | |
|---|---|
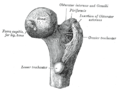
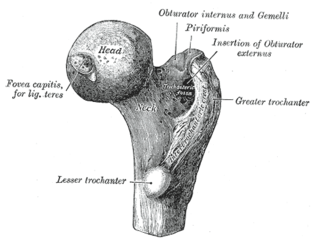
 Upper extremity of left femur viewed from behind showing head, neck, and the greater, lesser trochanter, intertrochanteric crest and trochanteric fossa | |
 Upper extremity of left femur viewed from behind showing head, neck, and the greater, lesser trochanter and intertrochanteric line | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | extremitas proximalis ossis femoris |
| FMA | 32841 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The upper extremity, proximal extremity or superior epiphysis of the femur is the part of the femur closest to the pelvic bone and the trunk. It contains the following structures:
- Femoral head including the fovea
- Femur neck
- Greater trochanter
- Lesser trochanter
- Intertrochanteric line
- Intertrochanteric crest
- Trochanteric fossa
- Linea quadrata
- Quadrate tubercle
The head of femur, which articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvic bone, composes two-thirds of a sphere. It has a small groove or fovea, connected through the round ligament to the sides of the acetabular notch. The head of the femur is connected to the shaft through the neck or collum. The neck is 4–5 cm. long and the diameter is smallest front to back and compressed at its middle. The collum forms an angle with the shaft in about 130 degrees. This angle is highly variant. In the infant it is about 150 degrees and in old age reduced to 120 degrees in average. An abnormal increase in the angle is known as coxa valga and an abnormal reduction is called coxa vara. Both the head and neck of the femur is vastly embedded in the hip musculature and can not be directly palpated. In skinny people with the thigh laterally rotated the head of the femur can be felt deep as a resistance profound (deep) for the femoral artery. [1]
In the transition area between the head and neck is quite rough due to attachment of muscles and the hip joint capsule. Here the two trochanters, greater and lesser trochanter, is found. The greater trochanter is almost box-shaped and is the most lateral prominent of the femur. The highest point of the greater trochanter is located higher than the collum and reaches the midpoint of the hip joint. The greater trochanter can easily be felt. The trochanteric fossa is a deep depression bounded posteriorly by the intertrochanteric crest on medial surface of the greater trochanter. Anterior and superior to the trochanteric fossa is a shallower depression known as the Unnamed Fossa. The Unnamed Fossa is the insertion point of the Superior Gemellus, Obturator Internus and Inferior Gemellus, which all act as lateral rotators of the thigh. The lesser trochanter is a cone-shaped extension of the lowest part of the femur neck. The two trochanters are joined by the intertrochanteric crest on the back side and by the intertrochanteric line on the front. [1]
A slight ridge is sometimes seen commencing about the middle of the intertrochanteric crest, and reaching vertically downward for about 5 cm. along the back part of the body: it is called the linea quadrata (or quadrate line).
About the junction of the upper one-third and lower two-thirds on the intertrochanteric crest is the quadrate tubercle located. The size of the tubercle varies and it is not always located on the intertrochanteric crest and that also adjacent areas can be part of the quadrate tubercle, such as the posterior surfare of the greater trochanter or the neck of the femur. In a small anatomical study it was shown that the epiphysial line passes directly through the quadrate tubercle. [2]