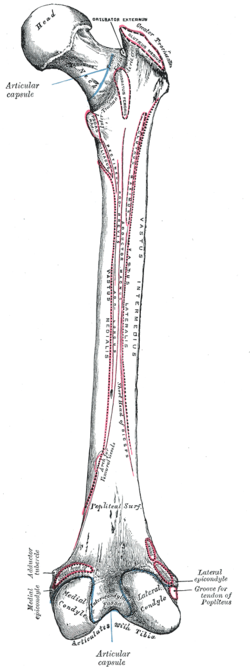
The human leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.
The femur, or thigh bone is the only bone in the thigh. The thigh is the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in the human body. Its thick fleshy mass, in a quadrilateral shape, forms the prominence of the buttocks. The other gluteal muscles are the medius and minimus, and sometimes informally these are collectively referred to as the glutes.
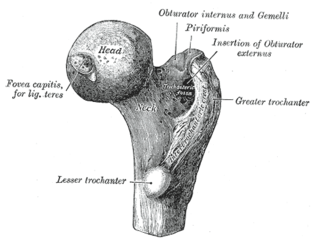
The greater trochanter of the femur is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence and a part of the skeletal system.

The pectineus muscle is a flat, quadrangular muscle, situated at the anterior (front) part of the upper and medial (inner) aspect of the thigh. The pectineus muscle is the most anterior adductor of the hip. The muscle's primary action is hip flexion; it also produces adduction and internal rotation of the hip.
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion and is activated by a separate nerve.

The adductor brevis is a muscle in the thigh situated immediately deep to the pectineus and adductor longus. It belongs to the adductor muscle group. The main function of the adductor brevis is to pull the thigh medially. The adductor brevis and the rest of the adductor muscle group is also used to stabilize left to right movements of the trunk, when standing on both feet, or to balance when standing on a moving surface. The adductor muscle group is used pressing the thighs together to ride a horse, and kicking with the inside of the foot in soccer or swimming. Last, they contribute to flexion of the thigh when running or against resistance.

The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.
The semimembranosus muscle is the most medial of the three hamstring muscles in the thigh. It is so named because it has a flat tendon of origin. It lies posteromedially in the thigh, deep to the semitendinosus muscle. It extends the hip joint and flexes the knee joint.
The linea aspera is a ridge of roughened surface on the posterior surface of the shaft of the femur. It is the site of attachments of muscles and the intermuscular septum.

In human anatomy, the muscles of the hip joint are those muscles that cause movement in the hip. Most modern anatomists define 17 of these muscles, although some additional muscles may sometimes be considered. These are often divided into four groups according to their orientation around the hip joint: the gluteal group; the lateral rotator group; the adductor group; and the iliopsoas group.
The gluteal tuberosity is the lateral one of the three upward prolongations of the linea aspera of the femur, extending to the base of the greater trochanter. It serves as the principal insertion site for the gluteus maximus muscle.

In human anatomy, the lesser trochanter is a conical, posteromedial, bony projection from the shaft of the femur. it serves as the principal insertion site of the iliopsoas muscle.
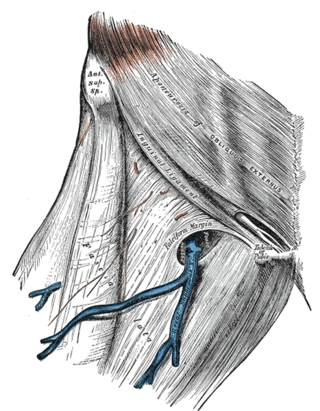
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular septum. The fascia lata is thickened at its lateral side where it forms the iliotibial tract, a structure that runs to the tibia and serves as a site of muscle attachment.

The upper extremity, proximal extremity or superior epiphysis of the femur is the part of the femur closest to the pelvic bone and the trunk. It contains the following structures:
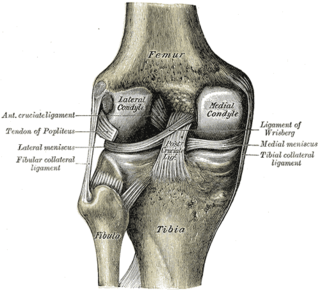
The lower extremity of femur is the lower end of the femur in human and other animals, closer to the knee. It is larger than the upper extremity of femur, is somewhat cuboid in form, but its transverse diameter is greater than its antero-posterior; it consists of two oblong eminences known as the lateral condyle and medial condyle.
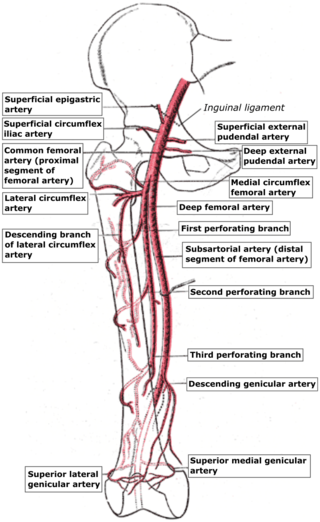
The perforating arteries are branches of the deep artery of the thigh, usually three in number, so named because they perforate the tendon of the adductor magnus to reach the back of the thigh. They pass backward near the linea aspera of the femur underneath the small tendinous arches of the adductor magnus muscle.

In human anatomy, the adductor minimus is a small and flat skeletal muscle in the thigh which constitutes the upper, lateral part of the adductor magnus muscle. It adducts and laterally rotates the femur.

The vastus muscles are three of the four muscles that make up the quadriceps femoris muscle of the thigh. The three muscles are the vastus intermedius, the vastus lateralis, and the vastus medialis located in the middle, on the outside, and inside of the thigh, respectively. The fourth muscle is the rectus femoris muscle a large fleshy muscle which covers the front and sides of the femur.