The deep femoral artery also known as the deep artery of the thigh, or profunda femoris artery, is a large branch of the femoral artery. It travels more deeply ("profoundly") than the rest of the femoral artery. It gives rise to the lateral circumflex femoral artery and medial circumflex femoral artery, and the perforating arteries, terminating within the thigh.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.

The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion and is activated by a separate nerve.

The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.

The gracilis muscle is the most superficial muscle on the medial side of the thigh. It is thin and flattened, broad above, narrow and tapering below.
The semimembranosus muscle is the most medial of the three hamstring muscles in the thigh. It is so named because it has a flat tendon of origin. It lies posteromedially in the thigh, deep to the semitendinosus muscle. It extends the hip joint and flexes the knee joint.

The semitendinosus is a long superficial muscle in the back of the thigh. It is so named because it has a very long tendon of insertion. It lies posteromedially in the thigh, superficial to the semimembranosus.

The popliteus muscle in the leg is used for unlocking the knees when walking, by laterally rotating the femur on the tibia during the closed chain portion of the gait cycle. In open chain movements, the popliteus muscle medially rotates the tibia on the femur. It is also used when sitting down and standing up. It is the only muscle in the posterior (back) compartment of the lower leg that acts just on the knee and not on the ankle. The gastrocnemius muscle acts on both joints.
The common fibular nerve is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides at the knee into two terminal branches: the superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve, which innervate the muscles of the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg respectively. When the common fibular nerve is damaged or compressed, foot drop can ensue.
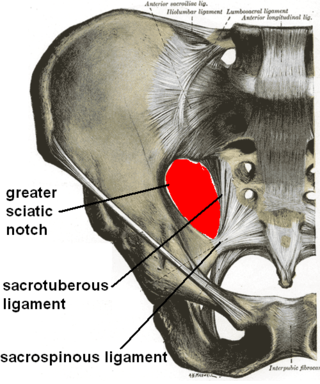
The sacrotuberous ligament is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends.

The medial meniscus is a fibrocartilage semicircular band that spans the knee joint medially, located between the medial condyle of the femur and the medial condyle of the tibia. It is also referred to as the internal semilunar fibrocartilage. The medial meniscus has more of a crescent shape while the lateral meniscus is more circular. The anterior aspects of both menisci are connected by the transverse ligament. It is a common site of injury, especially if the knee is twisted.

The lateral meniscus is a fibrocartilaginous band that spans the lateral side of the interior of the knee joint. It is one of two menisci of the knee, the other being the medial meniscus. It is nearly circular and covers a larger portion of the articular surface than the medial. It can occasionally be injured or torn by twisting the knee or applying direct force, as seen in contact sports.

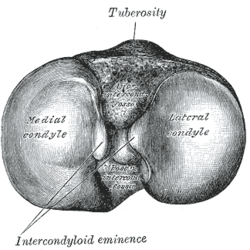
The medial condyle is the medial portion of the upper extremity of tibia.

The medial epicondyle of the femur is an epicondyle, a bony protrusion, located on the medial side of the femur at its distal end.

The anterior ligament of the lateral malleolus is a flat, trapezoidal band of fibers, broader below than above, which extends obliquely downward and lateralward between the adjacent margins of the tibia and fibula, on the front aspect of the syndesmosis.

The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection when the patella is fully ossified.
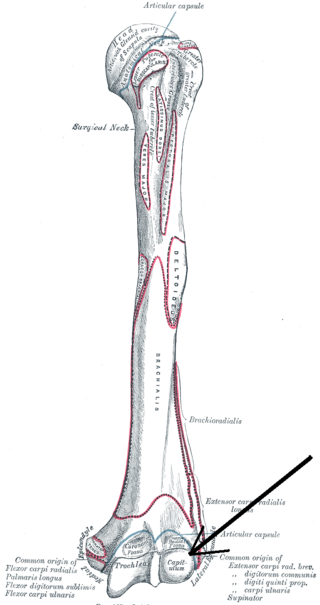
In human anatomy of the arm, the capitulum of the humerus is a smooth, rounded eminence on the lateral portion of the distal articular surface of the humerus. It articulates with the cup-shaped depression on the head of the radius, and is limited to the front and lower part of the bone.
The anterolateral ligament (ALL) is a ligament on the lateral aspect of the human knee, anterior to the fibular collateral ligament.