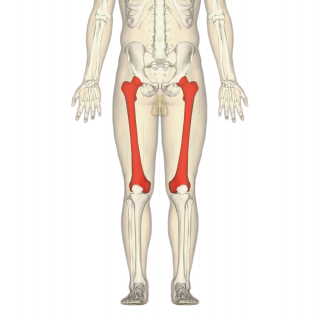
The femur, or thigh bone is the only bone in the thigh. The thigh is the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.

In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.

The metatarsal bones or metatarsus are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones and the phalanges (toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side : the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal. The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. A bovine hind leg has two metatarsals.
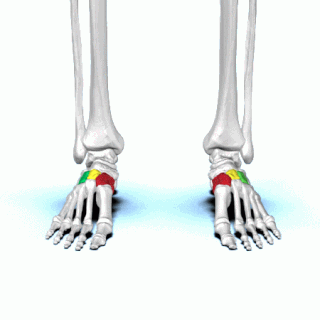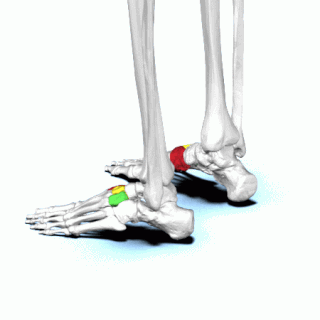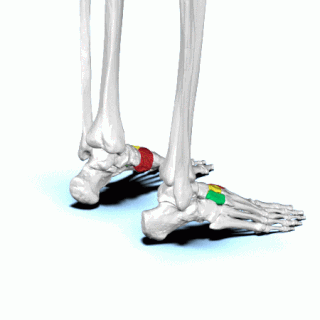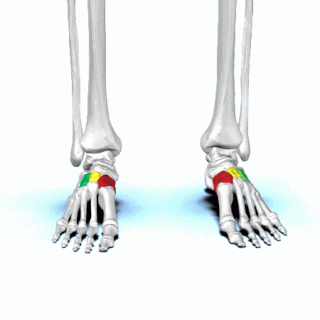
There are three cuneiform ("wedge-shaped") bones in the human foot:

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei of the foot are four muscles situated between the metatarsal bones.

The adductor muscles of the hip are a group of muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh mostly used for bringing the thighs together.

The lateral rotator group is a group of six small muscles of the hip which all externally (laterally) rotate the femur in the hip joint. It consists of the following muscles: piriformis, gemellus superior, obturator internus, gemellus inferior, quadratus femoris and the obturator externus.
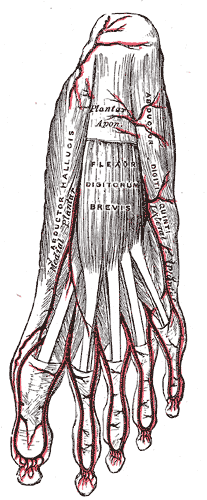
The abductor digiti minimi is a muscle which lies along the lateral (outer) border of the foot, and is in relation by its medial margin with the lateral plantar artery, vein and nerves.

The pubic arch, also referred to as the ischiopubic arch, is part of the pelvis. It is formed by the convergence of the inferior rami of the ischium and pubis on either side, below the pubic symphysis. The angle at which they converge is known as the subpubic angle.

The upper extremity, proximal extremity or superior epiphysis of the femur is the part of the femur closest to the pelvic bone and the trunk. It contains the following structures:

The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand.
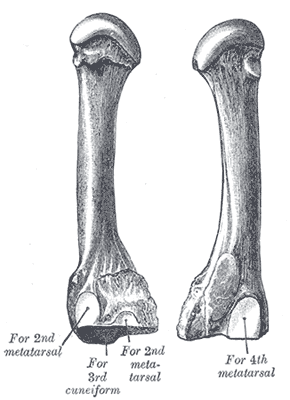
The third metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is the second longest metatarsal. The longest being the second metatarsal. The third metatarsal is analogous to the third metacarpal bone in the hand

The second metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is the longest of the metatarsal bones, being prolonged backward and held firmly into the recess formed by the three cuneiform bones. The second metatarsal forms joints with the second proximal phalanx through the metatarsophalangeal joint, the cuneiform bones, third metatarsal and occasionally the first metatarsal bone.

The first metatarsal bone is the bone in the foot just behind the big toe. The first metatarsal bone is the shortest of the metatarsal bones and by far the thickest and strongest of them.
The anserine bursa is a sub muscular bursa located deep to the pes anserinus on the anteromedial proximal tibia. Pes anserine bursitis is a common inflammatory condition of the anserine bursa.

The iliopectineal bursa or the iliopsoas bursa is a large synovial bursa that separates the external surface of the hip joint capsule from the normally just the tendon of the iliopsoas muscle.
The femoral-tibial angle is the angle between the femur and tibia.


























