The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males.
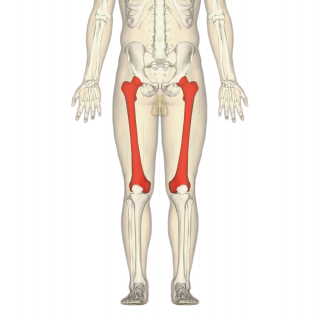
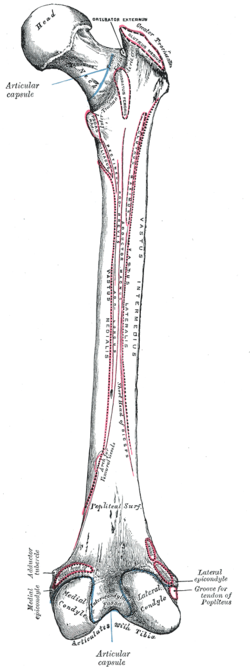
The femur, or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as mice, cats, birds and dogs, but not in whales, or most reptiles.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.

The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.

In vertebrate anatomy, hip refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.

The quadratus femoris is a flat, quadrilateral skeletal muscle. Located on the posterior side of the hip joint, it is a strong external rotator and adductor of the thigh, but also acts to stabilize the femoral head in the acetabulum. Quadratus femoris use in the Meyer's muscle pedicle grafting to prevent avascular necrosis of femur head.

The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.

The vastus intermedius (Cruraeus) arises from the front and lateral surfaces of the body of the femur in its upper two-thirds, sitting under the rectus femoris muscle and from the lower part of the lateral intermuscular septum. Its fibers end in a superficial aponeurosis, which forms the deep part of the quadriceps femoris tendon.

The semitendinosus is a long superficial muscle in the back of the thigh. It is so named because it has a very long tendon of insertion. It lies posteromedially in the thigh, superficial to the semimembranosus.
The linea aspera is a ridge of roughened surface on the posterior surface of the shaft of the femur. It is the site of attachments of muscles and the intermuscular septum.

The lesser trochanter is a conical posteromedial bony projection of the femoral shaft. it serves as the principal insertion site of the iliopsoas muscle.

The upper extremity, proximal extremity or superior epiphysis of the femur is the part of the femur closest to the pelvic bone and the trunk. It contains the following structures:
The body of femur is the almost cylindrical, long part of the femur. It is a little broader above than in the center, broadest and somewhat flattened from before backward below. It is slightly arched, so as to be convex in front, and concave behind, where it is strengthened by a prominent longitudinal ridge, the linea aspera.
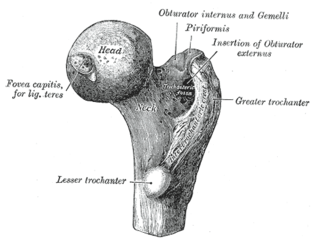
The intertrochanteric crest is a prominent bony ridge upon the posterior surface of the femur at the junction of the neck and the shaft of the femur. It extends between the greater trochanter superiorly, and the lesser trochanter inferiorly.

In human anatomy, the adductor minimus is a small and flat skeletal muscle in the thigh which constitutes the upper, lateral part of the adductor magnus muscle. It adducts and laterally rotates the femur.

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

The vastus muscles are three of the four muscles that make up the quadriceps femoris muscle of the thigh. The three muscles are the vastus intermedius, the vastus lateralis, and the vastus medialis located in the middle, on the outside, and inside of the thigh, respectively. The fourth muscle is the rectus femoris muscle a large fleshy muscle which covers the front and sides of the femur.