
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.

The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones and the phalanges (toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side : the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal. The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. A bovine hind leg has two metatarsals.
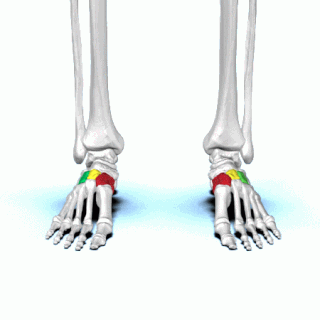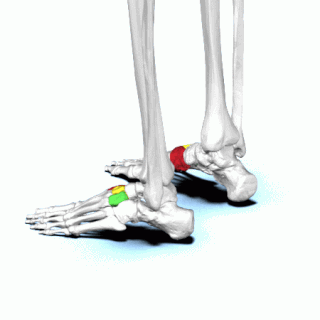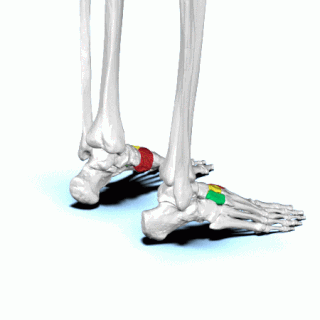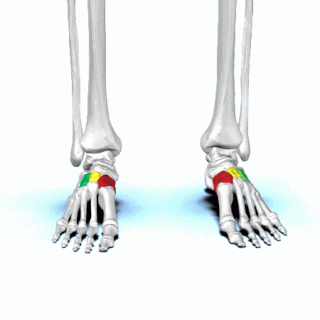
There are three cuneiform ("wedge-shaped") bones in the human foot:

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals.

The Maisonneuve fracture is a spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula associated with a tear of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis and the interosseous membrane. There is an associated fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deep deltoid ligament of the ankle. This type of injury can be difficult to detect.

A Jones fracture is a broken bone in a specific part of the fifth metatarsal of the foot between the base and middle part that is known for its high rate of delayed healing or nonunion. It results in pain near the midportion of the foot on the outside. There may also be bruising and difficulty walking. Onset is generally sudden.

A Lisfranc injury, also known as Lisfranc fracture, is an injury of the foot in which one or more of the metatarsal bones are displaced from the tarsus.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.

The calcaneocuboid joint is the joint between the calcaneus and the cuboid bone.

The tarsometatarsal joints are arthrodial joints in the foot. The tarsometatarsal joints involve the first, second and third cuneiform bones, the cuboid bone and the metatarsal bones. The eponym of Lisfranc joint is 18th–19th-century surgeon and gynecologist Jacques Lisfranc de St. Martin.

The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand.

A calcaneal fracture is a break of the calcaneus. Symptoms may include pain, bruising, trouble walking, and deformity of the heel. It may be associated with breaks of the hip or back.

Cuboid syndrome or cuboid subluxation describes a condition that results from subtle injury to the calcaneocuboid joint and ligaments in the vicinity of the cuboid bone, one of seven tarsal bones of the human foot.

Toddler's fractures are bone fractures of the distal (lower) part of the shin bone (tibia) in toddlers and other young children. The fracture is found in the distal two thirds of the tibia in 95% of cases, is undisplaced and has a spiral pattern. It occurs after low-energy trauma, sometimes with a rotational component.

A nasal fracture, commonly referred to as a broken nose, is a fracture of one of the bones of the nose. Symptoms may include bleeding, swelling, bruising, and an inability to breathe through the nose. They may be complicated by other facial fractures or a septal hematoma.
Chopart's fracture–dislocation is a dislocation of the mid-tarsal joints of the foot, often with associated fractures of the calcaneus, cuboid and navicular.

A broken toe is a type of bone fracture. Symptoms include pain when the toe is touched near the break point, or compressed along its length. There may be bruising, swelling, stiffness, or displacement of the broken bone ends from their normal position.

Mueller–Weiss syndrome, also known as Mueller–Weiss disease, is a rare idiopathic degenerative disease of the adult navicular bone characterized by progressive collapse and fragmentation, leading to mid- and hindfoot pain and deformity. It is most commonly seen in females, ages 40–60. Characteristic imaging shows lateral navicular collapse. This disease had been historically considered to be a form of adult onset osteonecrosis, with blood flow cutoff to the navicular.


















