| Tibialis posterior muscle | |
|---|---|
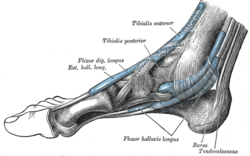 The mucous sheaths of the tendons around the ankle. Medial aspect. (Tibialis posterior labeled at top center.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Tibia and fibula |
| Insertion | Navicular and medial cuneiform bone |
| Artery | Posterior tibial artery |
| Nerve | Tibial nerve |
| Actions | Inversion of the foot and plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle |
| Antagonist | Fibularis brevis and longus, antagonist to the inversion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus tibialis posterior |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.051 |
| TA2 | 2666 |
| FMA | 51099 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The tibialis posterior muscle is the most central of all the leg muscles, and is located in the deep posterior compartment of the leg. It is the key stabilizing muscle of the lower leg.







