| Fibularis muscles | |
|---|---|
 Fibularis (peroneus) muscles | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus fibularis |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The fibularis muscles (also called peroneus muscles or peroneals) are a group of muscles in the lower leg.
| Fibularis muscles | |
|---|---|
 Fibularis (peroneus) muscles | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus fibularis |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The fibularis muscles (also called peroneus muscles or peroneals) are a group of muscles in the lower leg.
The muscle group is normally composed of three muscles: fibularis longus, fibularis brevis, and fibularis tertius. [1]
The fibularis longus and fibularis brevis are located in the lateral compartment of the leg and are supplied by the fibular artery and the superficial fibular nerve. The fibularis tertius is located in the anterior compartment of the leg and is supplied by the anterior tibial artery and the deep fibular nerve. While all three muscles move the sole of the foot outward, away from the midline of the body (eversion), the longus and brevis extend the foot downward away from the body (plantar flexion), whereas the tertius muscle pulls the foot upward toward the body (dorsiflexion).
| Name | Compartment | Action | Nerve | Artery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibularis longus | lateral compartment | eversion and plantar flexion | superficial fibular nerve | fibular artery |
| Fibularis brevis | lateral compartment | eversion and plantar flexion | superficial fibular nerve | fibular artery |
| Fibularis tertius | anterior compartment | eversion and dorsiflexion | deep fibular nerve | anterior tibial artery |
The fibularis muscles are highly variable. Several variants are occasionally present, including the peroneus digiti minimi and the peroneus quartus. [2] The quartus is more closely associated with the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus and may send a small tendon to the fifth (or little) toe. [3]
Terminologia Anatomica designates "fibularis" as the preferred word over "peroneus". [4]

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. There are 60 bones in each leg.

The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibres from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.
The ankle, the talocrural region or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.
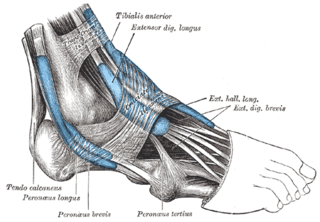
The extensor digitorum longus is a pennate muscle, situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg.

The extensor digitorum brevis muscle is a muscle on the upper surface of the foot that helps extend digits 2 through 4.

In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.

In human anatomy, the fibularis tertius is a muscle in the anterior compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to pull the foot upward toward the body (dorsiflexion).
The common fibular nerve is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides at the knee into two terminal branches: the superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve, which innervate the muscles of the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg respectively. When the common fibular nerve is damaged or compressed, foot drop can ensue.

The superficial fibular nerve is a mixed nerve that provides motor innervation to the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles, and sensory innervation to skin over the antero-lateral aspect of the leg along with the greater part of the dorsum of the foot.

The deep fibular nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.

In humans, the sole of the foot is anatomically referred to as the plantar aspect.

The superior extensor retinaculum of the foot is the upper part of the extensor retinaculum of foot which extends from the ankle to the heelbone.

The anterior compartment of the leg is a fascial compartment of the lower leg. It contains muscles that produce dorsiflexion and participate in inversion and eversion of the foot, as well as vascular and nervous elements, including the anterior tibial artery and veins and the deep fibular nerve.

The lateral compartment of the leg is a fascial compartment of the lower leg. It contains muscles which make eversion and plantarflexion of the foot.
A compartment syndrome is an increased pressure within a muscular compartment that compromises the circulation to the muscles.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk.