The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei of the foot are four muscles situated between the metatarsal bones.
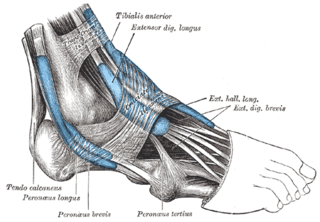
The extensor digitorum longus is a pennate muscle, situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg.

The extensor digitorum brevis muscle is a muscle on the upper surface of the foot that helps extend digits 2 through 4.

In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.
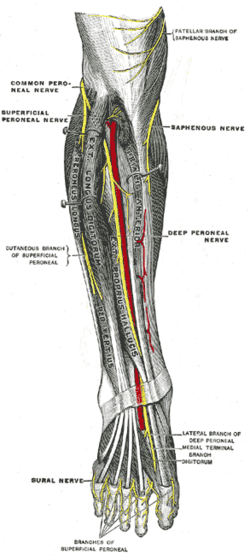
The common fibular nerve is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides at the knee into two terminal branches: the superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve, which innervate the muscles of the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg respectively. When the common fibular nerve is damaged or compressed, foot drop can ensue.

The extensor hallucis brevis is a muscle on the top of the foot that helps to extend the big toe.
The plantar nerves are a pair of nerves innervating the sole of the foot. They arise from the posterior branch of the tibial nerve.

The deep fibular nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.

In humans, the sole of the foot is anatomically referred to as the plantar aspect.

The fibularis muscles are a group of muscles in the lower leg.
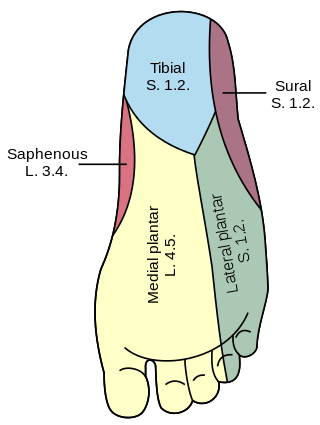
The saphenous nerve is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. It is derived from the lumbar plexus (L3-L4). It is a strictly sensory nerve, and has no motor function. It commences in the proximal (upper) thigh and travels along the adductor canal. Upon exiting the adductor canal, the saphenous nerve terminates by splitting into two terminal branches: the sartorial nerve, and the infrapatellar nerve. The saphenous nerve is responsible for providing sensory innervation to the skin of the anteromedial leg.

The intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve is the smaller and more lateral one of the two terminal branches of the superficial fibular nerve. It passes over the third intermetatarsal space before itself bifurcating into two terminal branches: the lateral dorsal digital nerve of the third toe, and the medial dorsal digital nerve of the fourth toe.

The medial dorsal cutaneous nerve is the more medial one of the two terminal branches of the superficial fibular nerve. Through its branches, it provides innervation to parts of the dorsal aspects of the first, second, and third toes.

The lateral sural cutaneous nerve of the lumbosacral plexus supplies the skin on the posterior and lateral surfaces of the leg. The lateral sural cutaneous nerve originates from the common fibular nerve(L4-S2) and is the terminal branch of the common fibular nerve.

Cutaneous innervation of the lower limbs is the nerve supply to areas of the skin of the lower limbs which are supplied by specific cutaneous nerves.

Dorsal digital nerves of foot are branches of the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, sural nerve and deep fibular nerve.