The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the arm, forearm and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects.

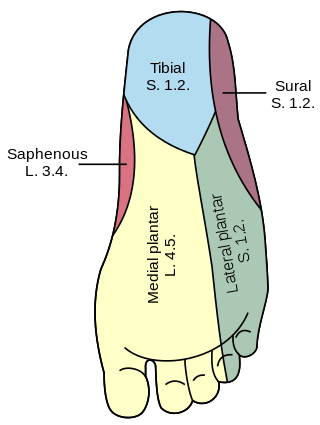
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The opponens digiti minimi is a muscle in the hand. It is of a triangular form, and placed immediately beneath the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis. It is one of the three hypothenar muscles that control the little finger.
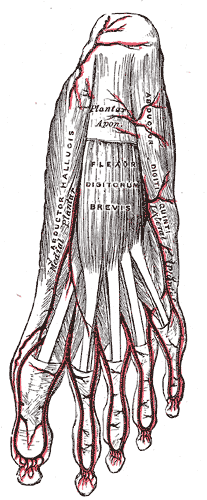
The flexor digitorum brevis is a muscle which lies in the middle of the sole of the foot, immediately above the central part of the plantar aponeurosis, with which it is firmly united.
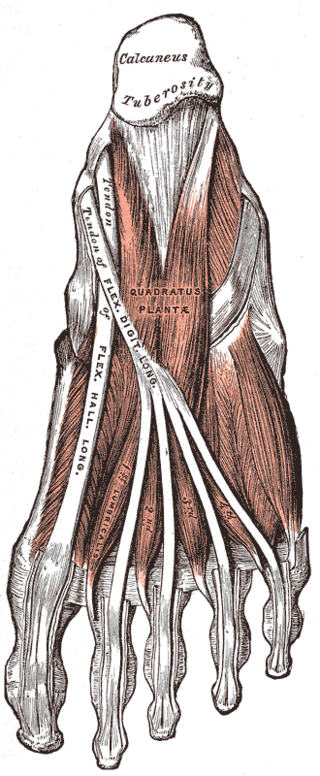
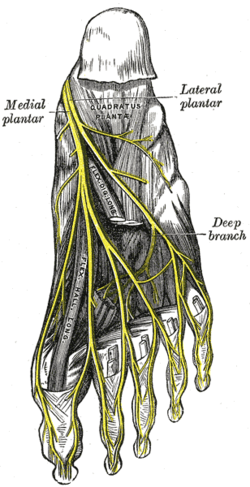
The quadratus plantae is separated from the muscles of the first layer by the lateral plantar vessels and nerve. It acts to aid in flexing the 2nd to 5th toes and is one of the few muscles in the foot with no homolog in the hand.
The plantar nerves are a pair of nerves innervating the sole of the foot. They arise from the posterior branch of the tibial nerve.

The hypothenar muscles are a group of three muscles of the palm that control the motion of the little finger.

The abductor digiti minimi is a muscle which lies along the lateral (outer) border of the foot, and is in relation by its medial margin with the lateral plantar artery, vein and nerves.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.

The flexor digiti minimi brevis is a hypothenar muscle in the hand that flexes the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint. It lies lateral to the abductor digiti minimi when the hand is in anatomical position.

In humans, the sole of the foot is anatomically referred to as the plantar aspect.

The medial plantar nerve is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve, which accompanies the medial plantar artery.

The lateral plantar artery, much larger than the medial, passes obliquely lateralward and forward to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The cervical spinal nerve 8 (C8) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment.

The superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into a proper and a common plantar digital nerve: