
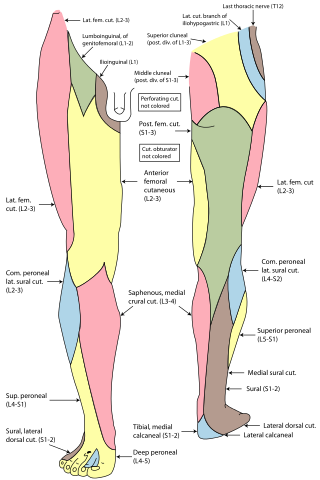
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The superficial fibular nerve is a mixed nerve that provides motor innervation to the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles, and sensory innervation to skin over the antero-lateral aspect of the leg along with the greater part of the dorsum of the foot.

The deep fibular nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.

The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a sensory nerve of the thigh. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It supplies the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh, leg, buttock, and also the perineum.

The medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm is a sensory branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus derived from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C8-T1. It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the medial forearm and skin overlying the olecranon. It descends through the (upper) arm within the brachial fascia alongside the basilic vein, then divides into an anterior branch and a posterior branch upon emerging from the brachial fascia; the two terminal branches travel as far distally as the wrist.

The medial brachial cutaneous nerve is a sensory branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus derived from spinal nerves C8-T1. It provides sensory innervation to the medial arm. It descends accompanied by the basilic vein.

The intercostobrachial nerve is the name applied to the lateral cutaneous branch of the second intercostal nerve. It arises anterior to the long thoracic nerve. It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the axilla, and a variable region of the medial side of the upper arm.

The medial plantar nerve is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve, which accompanies the medial plantar artery.

The superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm is the continuation of the posterior branch of the axillary nerve, after it pierces the deep fascia. It contains axons from C5-C6 ventral rami.

The posterior cutaneous nerve of arm is a branch of the radial nerve that provides sensory innervation for much of the skin on the back of the arm. It arises in the axilla.
A cutaneous nerve is a nerve that provides nerve supply to the skin.
The saphenous nerve is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. It is derived from the lumbar plexus (L3-L4). It is a strictly sensory nerve, and has no motor function. It commences in the proximal (upper) thigh and travels along the adductor canal. Upon exiting the adductor canal, the saphenous nerve terminates by splitting into two terminal branches: the sartorial nerve, and the infrapatellar nerve. The saphenous nerve is responsible for providing sensory innervation to the skin of the anteromedial leg.

The intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve is the smaller and more lateral one of the two terminal branches of the superficial fibular nerve. It passes over the third intermetatarsal space before itself bifurcating into two terminal branches: the lateral dorsal digital nerve of the third toe, and the medial dorsal digital nerve of the fourth toe.

The medial dorsal cutaneous nerve is the more medial one of the two terminal branches of the superficial fibular nerve. Through its branches, it provides innervation to parts of the dorsal aspects of the first, second, and third toes.

The medial sural cutaneous nerve(L4-S3) is a sensory nerve of the leg. It supplies cutaneous innervation the posteromedial leg.
The anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve consist of the following nerves: intermediate cutaneous nerve and medial cutaneous nerve.
The cutaneous branch of the obturator nerve is an occasional continuation of the communicating branch to the femoral medial cutaneous branches and saphenous branches of the femoral to the thigh and leg. When present it emerges from beneath the distal/inferior border of the adductor longus muscle and descends along the posterior margin of the sartorius muscle to the medial side of the knee where it pierces the deep fascia and communicates with the saphenous nerve. When present, it provides sensory innervation to the skin of proximal/superior half of the medial side of the leg.

Cutaneous innervation of the lower limbs is the nerve supply to areas of the skin of the lower limbs which are supplied by specific cutaneous nerves.

Cutaneous innervation of the upper limbs is the nerve supply to areas of the skin of the upper limbs which are supplied by specific cutaneous nerves.

Dorsal digital nerves of foot are branches of the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, sural nerve and deep fibular nerve.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











