
The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

The pectineus muscle is a flat, quadrangular muscle, situated at the anterior (front) part of the upper and medial (inner) aspect of the thigh. The pectineus muscle is the most anterior adductor of the hip. The muscle's primary action is hip flexion; it also produces adduction and internal rotation of the hip.

The external obturator muscle or obturator externus muscle is a flat, triangular muscle, which covers the outer surface of the anterior wall of the pelvis.

The adductor brevis is a muscle in the thigh situated immediately deep to the pectineus and adductor longus. It belongs to the adductor muscle group. The main function of the adductor brevis is to pull the thigh medially. The adductor brevis and the rest of the adductor muscle group is also used to stabilize left to right movements of the trunk, when standing on both feet, or to balance when standing on a moving surface. The adductor muscle group is used pressing the thighs together to ride a horse, and kicking with the inside of the foot in soccer or swimming. Last, they contribute to flexion of the thigh when running or against resistance.

In the human body, the adductor longus is a skeletal muscle located in the thigh. One of the adductor muscles of the hip, its main function is to adduct the thigh and it is innervated by the obturator nerve. It forms the medial wall of the femoral triangle.

The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.

The iliopsoas muscle refers to the joined psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name iliopsoas. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest flexor of the hip.

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.

The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus.

The adductor muscles of the hip are a group of muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh mostly used for bringing the thighs together.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.
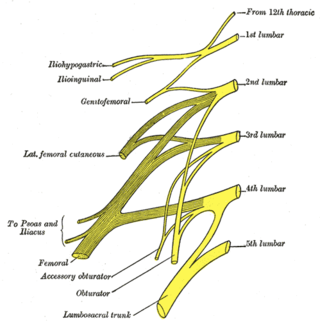
The lumbar nerves are the five pairs of spinal nerves emerging from the lumbar vertebrae. They are divided into posterior and anterior divisions.

The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.

The obturator artery is a branch of the internal iliac artery that passes antero-inferiorly on the lateral wall of the pelvis, to the upper part of the obturator foramen, and, escaping from the pelvic cavity through the obturator canal, it divides into an anterior branch and a posterior branch.

The nerve to obturator internus is a mixed nerve providing motor innervation to the obturator internus muscle and gemellus superior muscle, and sensory innervation to the hip joint. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It is one of the group of deep gluteal nerves.

The nerve to quadratus femoris is a nerve of the sacral plexus that provides motor innervation to the quadratus femoris muscle and gemellus inferior muscle, and an articular branch to the hip joint. The nerve leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen.
The anterior branch of the obturator nerve is a branch of the obturator nerve found in the pelvis and leg.

The gemelli muscles are the inferior gemellus muscle and the superior gemellus muscle, two small accessory fasciculi to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle. The gemelli muscles belong to the lateral rotator group of six muscles of the hip that rotate the femur in the hip joint.














