The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males.

Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being digitigrade. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being plantigrade; unguligrade animals are those that walk on hooves at the tips of their toes.

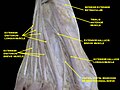
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
The common fibular nerve is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides at the knee into two terminal branches: the superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve, which innervate the muscles of the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg respectively. When the common fibular nerve is damaged or compressed, foot drop can ensue.

The superficial fibular nerve innervates the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles and the skin over the antero-lateral aspect of the leg along with the greater part of the dorsum of the foot.

The plantar nerves are a pair of nerves innervating the sole of the foot. They arise from the posterior branch of the tibial nerve.

The deep fibular nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.

The superficial branch of the radial nerve passes along the front of the radial side of the forearm to the commencement of its lower third. It is a sensory nerve.

The sole is the bottom of the foot.
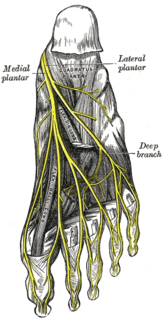
The medial plantar nerve is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve, which accompanies the medial plantar artery.

The plantar metatarsal arteries are four in number, arising from the convexity of the plantar arch. They run forward between the metatarsal bones and in contact with the Interossei. They are located in the fourth layer of the foot.
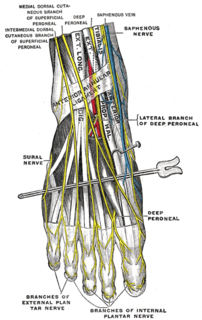
The intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, the smaller, passes along the lateral part of the dorsum of the foot, and divides into dorsal digital branches, which supply the contiguous sides of the third and fourth, and of the fourth and fifth toes.

The medial dorsal cutaneous nerve passes in front of the ankle-joint, and divides into two dorsal digital branches, one of which supplies the medial side of the great toe, the other, the adjacent side of the second and third toes.

Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific nerve.

The lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve is a cutaneous branch of the foot.

The superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into a proper and a common plantar digital nerve:

The proper plantar digital nerves of lateral plantar nerve are nerves of the foot that arise from the superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve. The superficial branch splits into a proper digital nerve and a common digital nerve:

The common plantar digital nerves of lateral plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. The common digital nerve communicates with the third common digital branch of the medial plantar nerve and divides into two proper digital nerves which supply the adjoining sides of the fourth and fifth toes.

The proper plantar digital nerves of medial plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. They primarily arise from the medial plantar nerve's superficial and deep branches. The superficial branch of the medial plantar nerve turns into a proper digital nerve and is responsible for supplies the medial side of the great toe.

The common plantar digital nerves of medial plantar nerve are nerves of the foot. The three common digital nerves pass between the divisions of the plantar aponeurosis, and each splits into two proper digital nerves: