The perineum in mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx, including the perineal body and surrounding structures. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. This area is also known as the taint or gooch in American slang.
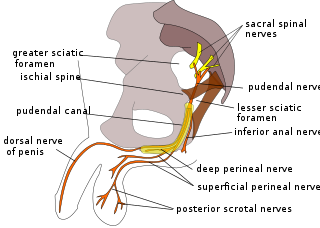
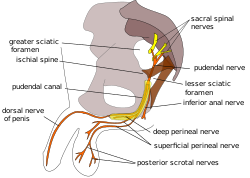
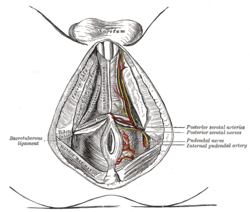
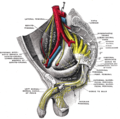
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a mixed nerve and also conveys sympathetic autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter.

The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis.

The bulbospongiosus muscles are a subgroup of the superficial muscles of the perineum. They have a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. In males, these muscles cover the bulb of the penis, while in females, they cover the vestibular bulbs.

The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia.

The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis.

The external anal sphincter is an oval tube of skeletal muscle fibers. Distally, it is adherent to the skin surrounding the margin of the anus. It exhibits a resting state of tonical contraction.
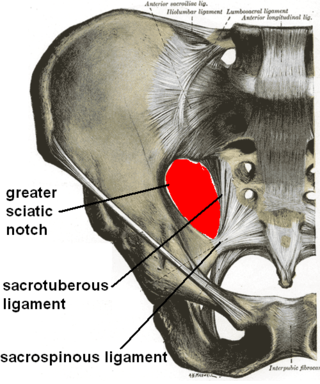
The sacrotuberous ligament is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends.

The inferior rectal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the lower third of the anal canal below the pectinate line.

The internal pudendal veins are a set of veins in the pelvis. They are the venae comitantes of the internal pudendal artery. Internal pudendal veins are enclosed by pudendal canal, with internal pudendal artery and pudendal nerve.

The pudendal canal is an anatomical structure formed by the obturator fascia lining the lateral wall of the ischioanal fossa. The internal pudendal artery and veins, and pudendal nerve pass through the pudendal canal, and the perineal nerve arises within it.

The membranous layer of the superficial fascia of the perineum is the deeper layer of the superficial perineal fascia. It is thin, aponeurotic in structure, and of considerable strength, serving to bind down the muscles of the root of the penis. Colles' fascia emerges from the perineal membrane, which divides the base of the penis from the prostate. Colles' fascia emerges from the inferior side of the perineal membrane and continues along the ventral (inferior) penis without covering the scrotum. It separates the skin and subcutaneous fat from the superficial perineal pouch.

The inferior rectal nerves usually branch from the pudendal nerve but occasionally arises directly from the sacral plexus; they cross the ischiorectal fossa along with the inferior rectal artery and veins, toward the anal canal and the lower end of the rectum, and is distributed to the sphincter ani externus and to the integument (skin) around the anus.

The dorsal artery of the penis is an artery on the top surface of the penis. It is a branch of the internal pudendal artery. It runs forward on the dorsum of the penis to the glans, where it divides into two branches to the glans penis and the foreskin (prepuce).

The transverse perineal muscles are the superficial and the deep transverse perineal muscles.

The deep perineal pouch is the anatomic space enclosed in part by the perineum and located superior to the perineal membrane.

The anal triangle is the posterior part of the perineum. It contains the anal canal.
The dorsal nerve of the clitoris is a nerve in females that branches off the pudendal nerve to innervate the clitoris. The nerve is important for female sexual pleasure, and it may play a role in clitoral erections.

The posterior labial nerves are branches of the pudendal nerve. They supply the female labia majora.

The deep branch of the perineal nerve is a nerve of the perineum. It is a branch of the perineal nerve, from the pudendal nerve. It supplies the superficial transverse perineal muscle, bulbospongiosus muscle, ischiocavernosus muscle, the bulb of penis, levator ani, and the external anal sphincter.