
The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. There are 60 bones in each leg.

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.

The ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna, one of the two long bones in the forearm. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

The extensor hallucis longus muscle is a thin skeletal muscle, situated between the tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus. It extends the big toe and dorsiflects the foot. It also assists with foot eversion and inversion.

The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.
In human anatomy, the dorsalis pedis artery is a blood vessel of the lower limb. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, and ends at the first intermetatarsal space. It carries oxygenated blood to the dorsal side of the foot. It is useful for taking a pulse. It is also at risk during anaesthesia of the deep peroneal nerve.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
The common fibular nerve is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides at the knee into two terminal branches: the superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve, which innervate the muscles of the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg respectively. When the common fibular nerve is damaged or compressed, foot drop can ensue.

The superficial fibular nerve is a mixed nerve that provides motor innervation to the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles, and sensory innervation to skin over the antero-lateral aspect of the leg along with the greater part of the dorsum of the foot.

The deep fibular nerve begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a lateral and a medial terminal branch.

The medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm is a sensory branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus derived from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C8-T1. It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the medial forearm and skin overlying the olecranon. It descends through the (upper) arm within the brachial fascia alongside the basilic vein, then divides into an anterior branch and a posterior branch upon emerging from the brachial fascia; the two terminal branches travel as far distally as the wrist.

In humans, the sole of the foot is anatomically referred to as the plantar aspect.
The saphenous nerve is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. It is derived from the lumbar plexus (L3-L4). It is a strictly sensory nerve, and has no motor function. It commences in the proximal (upper) thigh and travels along the adductor canal. Upon exiting the adductor canal, the saphenous nerve terminates by splitting into two terminal branches: the sartorial nerve, and the infrapatellar nerve. The saphenous nerve is responsible for providing sensory innervation to the skin of the anteromedial leg.

The intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve is the smaller and more lateral one of the two terminal branches of the superficial fibular nerve. It passes over the third intermetatarsal space before itself bifurcating into two terminal branches: the lateral dorsal digital nerve of the third toe, and the medial dorsal digital nerve of the fourth toe.
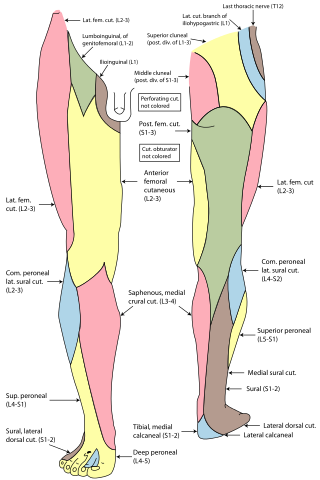
Cutaneous innervation of the lower limbs is the nerve supply to areas of the skin of the lower limbs which are supplied by specific cutaneous nerves.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
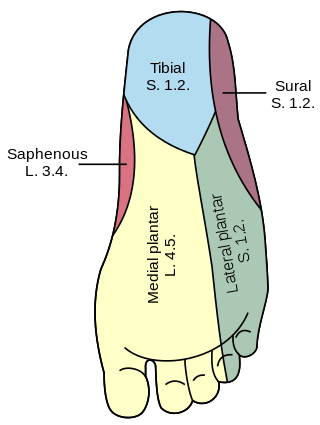
The lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve is the continuation/terminal sensory branch of the sural nerve, and is ultimately derived from the 1st sacral nerve (S1). It passes distally along the lateral part of the dorsum of foot. It gives rise to the lateral dorsal digital nerve of the 5th toe, and sometimes also the medial dorsal digital nerve of the 5th toe as well as the lateral dorsal digital nerve of the 4th toe.

Dorsal digital nerves of foot are branches of the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, sural nerve and deep fibular nerve.















