
The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
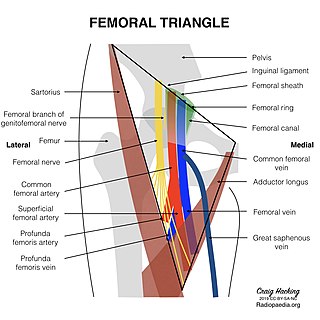
The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper third of the thigh. It is a subfascial space which appears as a triangular depression below the inguinal ligament when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated.

The pectineus muscle is a flat, quadrangular muscle, situated at the anterior (front) part of the upper and medial (inner) aspect of the thigh. The pectineus muscle is the most anterior adductor of the hip. The muscle's primary action is hip flexion; it also produces adduction and internal rotation of the hip.
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion and is activated by a separate nerve.

The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.

The vastus intermedius (Cruraeus) arises from the front and lateral surfaces of the body of the femur in its upper two-thirds, sitting under the rectus femoris muscle and from the lower part of the lateral intermuscular septum. Its fibers end in a superficial aponeurosis, which forms the deep part of the quadriceps femoris tendon.
The rectus femoris muscle is one of the four quadriceps muscles of the human body. The others are the vastus medialis, the vastus intermedius, and the vastus lateralis. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the patella by the quadriceps tendon.

The iliopsoas muscle refers to the joined psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name iliopsoas. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest flexor of the hip.
The linea aspera is a ridge of roughened surface on the posterior surface of the shaft of the femur. It is the site of attachments of muscles and the intermuscular septum.

The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.
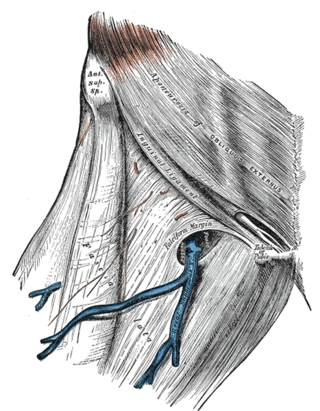
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular septum. The fascia lata is thickened at its lateral side where it forms the iliotibial tract, a structure that runs to the tibia and serves as a site of muscle attachment.

The lateral circumflex femoral artery is an artery in the upper thigh. It is usually a branch of the profunda femoris artery, and produces three branches. It is mostly distributed to the muscles of the lateral thigh, supplying arterial blood to muscles of the knee extensor group.

The adductor canal is an aponeurotic tunnel in the middle third of the thigh giving passage to parts of the femoral artery, vein, and nerve. It extends from the apex of the femoral triangle to the adductor hiatus.
The saphenous nerve is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. It is derived from the lumbar plexus (L3-L4). It is a strictly sensory nerve, and has no motor function. It commences in the proximal (upper) thigh and travels along the adductor canal. Upon exiting the adductor canal, the saphenous nerve terminates by splitting into two terminal branches: the sartorial nerve, and the infrapatellar nerve. The saphenous nerve is responsible for providing sensory innervation to the skin of the anteromedial leg.

The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves.

The posterior compartment of the thigh is one of the fascial compartments that contains the knee flexors and hip extensors known as the hamstring muscles, as well as vascular and nervous elements, particularly the sciatic nerve.

The vastus muscles are three of the four muscles that make up the quadriceps femoris muscle of the thigh. The three muscles are the vastus intermedius, the vastus lateralis, and the vastus medialis located in the middle, on the outside, and inside of the thigh, respectively. The fourth muscle is the rectus femoris muscle a large fleshy muscle which covers the front and sides of the femur.















