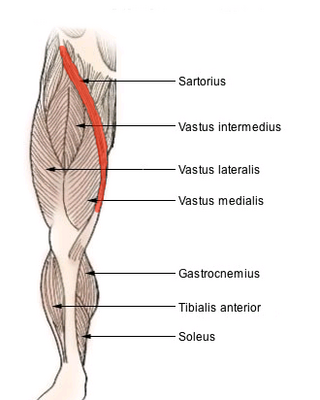
The sartorius muscle is the longest muscle in the human body. It is a long, thin, superficial muscle that runs down the length of the thigh in the anterior compartment.
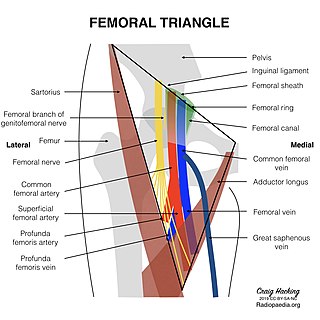
The femoral triangle is an anatomical region of the upper third of the thigh. It is a subfascial space which appears as a triangular depression below the inguinal ligament when the thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated.
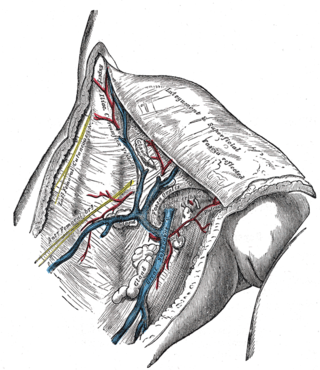
The great saphenous vein (GSV) or long saphenous vein is a large, subcutaneous, superficial vein of the leg. It is the longest vein in the body, running along the length of the lower limb, returning blood from the foot, leg and thigh to the deep femoral vein at the femoral triangle.

The external carotid artery is the major artery of the head and upper neck. It arises from the common carotid artery. It terminates by splitting into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland.

The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space behind (retro) the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal.

The genitofemoral nerve is a mixed branch of the lumbar plexus derived from anterior rami of L1-L2. It splits a genital branch and a femoral branch. It provides sensory innervation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. It also provides motor innervation to the cremaster muscle.

Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the groin. They are situated in the femoral triangle of the inguinal region. They are subdivided into two groups: the superficial inguinal lymph nodes and deep inguinal lymph nodes.

The popliteal vein is a vein of the lower limb. It is formed from the anterior tibial vein and the posterior tibial vein. It travels medial to the popliteal artery, and becomes the femoral vein. It drains blood from the leg. It can be assessed using medical ultrasound. It can be affected by popliteal vein entrapment.

In the human body, the femoral vein is the vein that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It is a deep vein that begins at the adductor hiatus as the continuation of the popliteal vein. The great saphenous vein, and the deep femoral vein drain into the femoral vein in the femoral triangle when it becomes known as the common femoral vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament where it becomes the external iliac vein. Its major tributaries are the deep femoral vein, and the great saphenous vein. The femoral vein contains valves.

In human anatomy, the left gastric artery arises from the celiac artery and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach before anastomosing with the right gastric artery. It also issues esophageal branches that supply lower esophagus and ascend through the esophageal hiatus to form anastomoses with the esophageal branches of thoracic part of aorta.

The gracilis muscle is the most superficial muscle on the medial side of the thigh. It is thin and flattened, broad above, narrow and tapering below.

In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.
In human anatomy, the inguinal region refers to either the groin or the lower lateral regions of the abdomen. It may also refer to:

The adductor canal is an aponeurotic tunnel in the middle third of the thigh giving passage to parts of the femoral artery, vein, and nerve. It extends from the apex of the femoral triangle to the adductor hiatus.
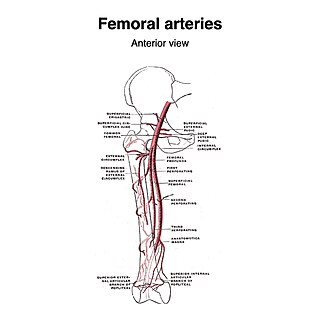
The superficial iliac circumflex artery, the smallest of the cutaneous branches of the femoral artery, arises close to the superficial epigastric artery, and, piercing the fascia lata, runs lateralward, parallel with the inguinal ligament, as far as the crest of the ilium.

The descending genicular artery arises from the femoral artery just before its passage through the adductor hiatus.
The saphenous nerve is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. It is derived from the lumbar plexus (L3-L4). It is a strictly sensory nerve, and has no motor function. It commences in the proximal (upper) thigh and travels along the adductor canal. Upon exiting the adductor canal, the saphenous nerve terminates by splitting into two terminal branches: the sartorial nerve, and the infrapatellar nerve. The saphenous nerve is responsible for providing sensory innervation to the skin of the anteromedial leg.

The membranous urethra or intermediate part of male urethra is the shortest, least dilatable, and, with the exception of the urinary meatus, the narrowest part of the urethra. It extends from the apex of the prostate proximally to the bulb of urethra distally. It measures some 12 mm in length. It traverses the pelvic floor. It is surrounded by the external urethral sphincter, which is in turn envelopped by the superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm.
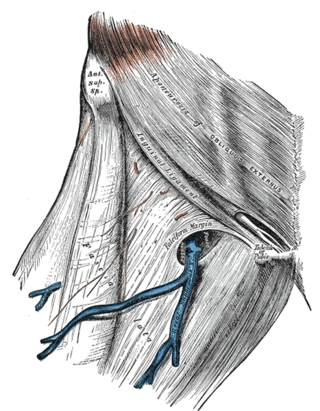
In anatomy, the saphenous opening is an oval opening in the upper mid part of the fascia lata of the thigh. It lies 3–4 cm below and lateral to the pubic tubercle and is about 3 cm long and 1.5 cm wide.

The urogenital hiatus is a large midline opening in the anteromedial part of the pelvic floor, extending between the pubis (anteriorly), and rectum (posteriorly). Each levator ani muscle forms either lateral border of the hiatus.

















