This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(June 2015) |
| Abductor digiti minimi muscle of foot | |
|---|---|
 First layer of the muscles of the sole (abductor digiti minimi visible at center right). | |
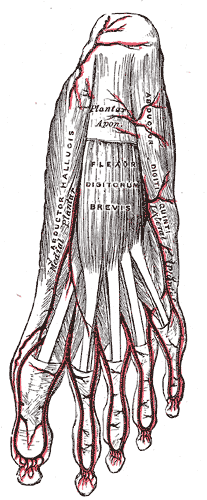 Superficial view of the plantar arteries (abductor digiti minimi visible at center right). | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Plantar aponeurosis |
| Insertion | Fifth toe or phalanges |
| Artery | Lateral plantar artery |
| Nerve | Lateral plantar nerve |
| Actions | Flexion and abduction of the fifth toe |
| Antagonist | Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus abductor digiti minimi pedis |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.063 |
| TA2 | 2679 |
| FMA | 37451 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The abductor digiti minimi (abductor minimi digiti, abductor digiti quinti or musculus abductor digiti V.) is a muscle which lies along the lateral (outer) border of the foot, [1] and is in relation by its medial margin with the lateral plantar artery, vein and nerves.
Contents
Its homolog in the arm is the abductor digiti minimi muscle in the hand.


