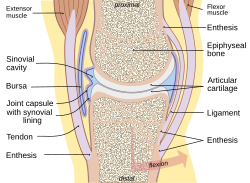
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.
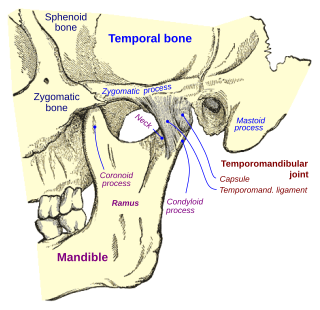
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the mandible below; it is from these bones that its name is derived. This joint is unique in that it is a bilateral joint that functions as one unit. Since the TMJ is connected to the mandible, the right and left joints must function together and therefore are not independent of each other.

A joint or articulation is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

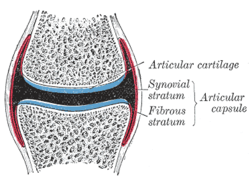
The synovial membrane is a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints and tendon sheath. It makes direct contact with the fibrous membrane on the outside surface and with the synovial fluid lubricant on the inside surface. In contact with the synovial fluid at the tissue surface are many rounded macrophage-like synovial cells and also type B cells, which are also known as fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). Type A cells maintain the synovial fluid by removing wear-and-tear debris. As for the FLS, they produce hyaluronan, as well as other extracellular components in the synovial fluid.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.
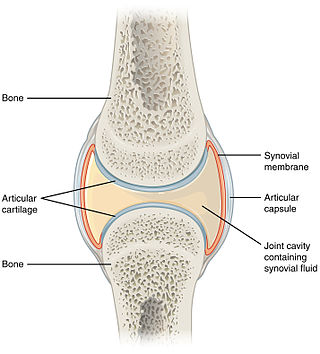
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer of fibrous membrane, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid.

The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones.

Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray in color, with a firm consistency and has a considerable amount of collagen. It contains no nerves or blood vessels, and its structure is relatively simple.

The acromioclavicular joint, or AC joint, is a joint at the top of the shoulder. It is the junction between the acromion and the clavicle. It is a plane synovial joint.

In vertebrate anatomy, hip refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.

The external obturator muscle, obturator externus muscle is a flat, triangular muscle, which covers the outer surface of the anterior wall of the pelvis.

The condyloid process or condylar process is the process on the human and other mammalian species' mandibles that ends in a condyle, the mandibular condyle. It is thicker than the coronoid process of the mandible and consists of two portions: the condyle and the constricted portion which supports it, the neck.

The sternoclavicular joint or sternoclavicular articulation is a synovial saddle joint between the manubrium of the sternum, and the clavicle, and the first costal cartilage. The joint possesses a joint capsule, and an articular disc, and is reinforced by multiple ligaments.
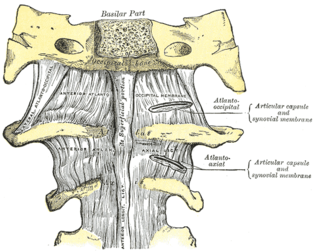
The atlanto-occipital joint is an articulation between the atlas bone and the occipital bone. It consists of a pair of condyloid joints. It is a synovial joint.

The intercarpal joints can be subdivided into three sets of joints : Those of the proximal row of carpal bones, those of the distal row of carpal bones, and those of the two rows with each other.

The articular capsule of the knee joint is the wide and lax joint capsule of the knee. It is thin in front and at the side, and contains the patella, ligaments, menisci, and bursae of the knee. The capsule consists of an inner synovial membrane, and an outer fibrous membrane separated by fatty deposits anteriorly and posteriorly.

The articular disk of the temporomandibular joint is a thin, oval plate made of non-vascular fibrous connective tissue located between the mandible's condyloid process and the cranium's mandibular fossa.

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors, physicians, and pharmacists.