
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora, also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora, they form the labia of the vulva.

The labia minora, also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin that are part of the primate vulva, extending outwards from the vaginal and urethral openings to encompass the vestibule. The labia minora are situated between the labia majora and together form the labia. They vary widely in size, color and shape from individual to individual.
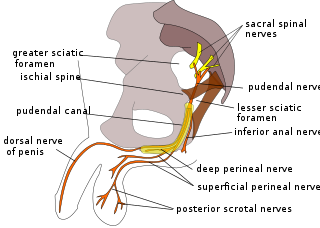
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a mixed nerve and also conveys sympathetic autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter.

The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia.

The labia are the major externally visible portions of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the labia majora are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts while the labia minora are the inner folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the urethral and vaginal openings.
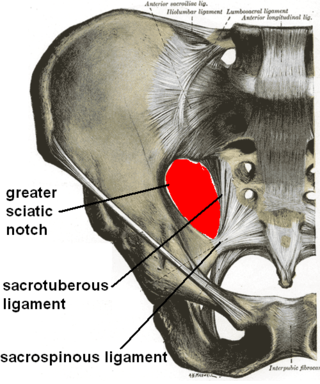
The sacrotuberous ligament is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends.

The inferior gluteal artery is a terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. It is distributed chiefly to the buttock and the back of the thigh.

The perineal nerve is a nerve of the pelvis. It arises from the pudendal nerve in the pudendal canal. It gives superficial branches to the skin, and a deep branch to muscles. It supplies the skin and muscles of the perineum. Its latency is tested with electrodes.

The posterior scrotal branches are two in number, medial and lateral. They are branches of the perineal nerve, which is itself a branch of the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve arises from spinal roots S2 through S4, travels through the pudendal canal on the fascia of the obturator internus muscle, and gives off the perineal nerve in the perineum. The major branch of the perineal nerve is the posterior scrotal/posterior labial.

The inferior rectal nerves usually branch from the pudendal nerve but occasionally arises directly from the sacral plexus; they cross the ischiorectal fossa along with the inferior rectal artery and veins, toward the anal canal and the lower end of the rectum, and is distributed to the sphincter ani externus and to the integument (skin) around the anus.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The deep external pudendal artery is one of the pudendal arteries that is more deeply seated than the superficial external pudendal artery, passes medially across the pectineus and the adductor longus muscles; it is covered by the fascia lata, which it pierces at the medial side of the thigh, and is distributed, in the male, to the integument of the scrotum and perineum, in the female to the labia majora; its branches anastomose with the scrotal or labial branches of the perineal artery.

The urogenital triangle is the anterior part of the perineum. In female mammals, it contains the vagina and associated parts of the internal genitalia.

The anal triangle is the posterior part of the perineum. It contains the anal canal.

The posterior labial nerves are branches of the pudendal nerve. They supply the female labia majora.

The posterior scrotal arteries are branches of the internal pudendal artery.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The pudendal arteries are a group of arteries which supply many of the muscles and organs of the pelvic cavity. The arteries include the internal pudendal artery, the superficial external pudendal artery, and the deep external pudendal artery.
Scrotal arteries may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.














