
The brachiocephalic artery, brachiocephalic trunk, or innominate artery is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm, head, and neck.
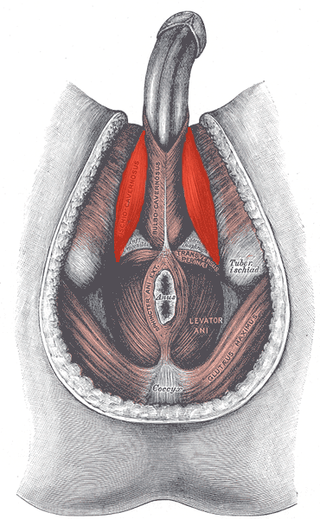
The ischiocavernosus muscle is a muscle just below the surface of the perineum, present in both men and women.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior and middle cerebral circulation.

The basilar artery is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood.

The common hepatic artery is a short blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, pylorus of the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and gallbladder.

The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) is one of three pairs of arteries that supplies blood to the cerebellum.
Appendicular can refer to:

The aortic arches or pharyngeal arch arteries are a series of six paired embryological vascular structures which give rise to the great arteries of the neck and head. They are ventral to the dorsal aorta and arise from the aortic sac.
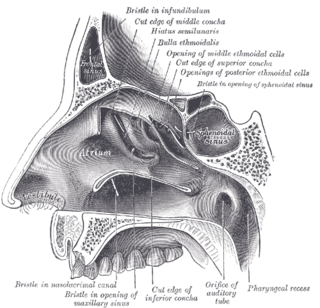
The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus in the body of the sphenoid bone. It is one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The two sphenoid sinuses are separated from each other by a septum. Each sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity via the opening of sphenoidal sinus. The two sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape, and are usually asymmetrical.

The superior gluteal artery is the terminal branch of the posterior division of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen before splitting into a superficial branch and a deep branch.

The right colic artery is an artery of the abdomen, a branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the ascending colon. It divides into two terminal branches - an ascending branch and a descending branch - which form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and ileocolic artery (respectively).

The ileocolic artery is the lowest branch arising from the concavity of the superior mesenteric artery. It supplies the cecum, ileum, and appendix.

In the anatomy of the human digestive tract, there are two colic flexures, or curvatures in the transverse colon. The right colic flexure is also known as the hepatic flexure, and the left colic flexure is also known as the splenic flexure. Note that "right" refers to the patient's anatomical right, which may be depicted on the left of a diagram.

The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible.

The sphenopalatine artery is an artery of the head, commonly known as the artery of epistaxis. It passes through the sphenopalatine foramen to reach the nasal cavity. It is the main artery of the nasal cavity.
The pulmonary plexus is an autonomic plexus formed from pulmonary branches of vagus nerve and the sympathetic trunk. The plexus is in continuity with the deep cardiac plexus.

The costocervical trunk arises from the upper and back part of the second part of subclavian artery, behind the scalenus anterior on the right side, and medial to that muscle on the left side.

The supratrochlear artery is one of the terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It arises within the orbit. It exits the orbit alongside the supratrochlear nerve. It contributes arterial supply to the skin, muscles and pericranium of the forehead.

The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries passing within an intercostal space. There are 9 anterior and 11 posterior intercostal arteries on each side of the body. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery and its terminal branch - the musculophrenic artery. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the supreme intercostal artery and thoracic aorta.

The superior mesenteric lymph nodes may be divided into three principal groups:



















