The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine.

The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.

In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.

A pancreaticoduodenectomy, also known as a Whipple procedure, is a major surgical operation most often performed to remove cancerous tumours from the head of the pancreas. It is also used for the treatment of pancreatic or duodenal trauma, or chronic pancreatitis. Due to the shared blood supply of organs in the proximal gastrointestinal system, surgical removal of the head of the pancreas also necessitates removal of the duodenum, proximal jejunum, gallbladder, and, occasionally, part of the stomach.

The celiacartery, also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta.
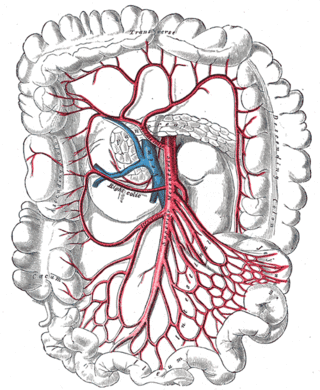
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas.

In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the distal transverse colon to the upper part of the anal canal. The regions supplied by the IMA are the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and part of the rectum.

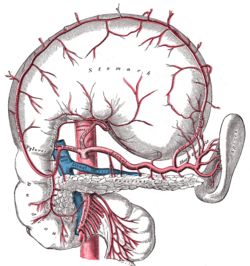
In human anatomy, the splenic artery or lienal artery, an older term, is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the spleen. It branches from the celiac artery, and follows a course superior to the pancreas. It is known for its tortuous path to the spleen.

The common hepatic artery is a short blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, pylorus of the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and gallbladder.

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

In human anatomy, the left gastric artery arises from the celiac artery and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach before anastomosing with the right gastric artery. It also issues esophageal branches that supply lower esophagus and ascend through the esophageal hiatus to form anastomoses with the esophageal branches of thoracic part of aorta.

The hepatic artery proper is the artery that supplies the liver and gallbladder. It raises from the common hepatic artery, a branch of the celiac artery.

The cystic artery is (usually) a branch of the right hepatic artery that provides arterial supply to the gallbladder and contributes arterial supply to the extrahepatic bile ducts.

The right gastroepiploic artery is one of the two terminal branches of the gastroduodenal artery. It runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the splenic artery.

The superior pancreaticoduodenal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the duodenum and pancreas.

The duodenal bulb is the initial, dilated portion of the duodenum just distal to the stomach; it begins at the pylorus and ends at the neck of the gallbladder. It is normally about 5 centimeters long.

The pancreatic branches or pancreatic arteries are numerous small vessels derived from the splenic artery as it runs behind the upper border of the pancreas, supplying its body and tail.

The hepatic plexus is a sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve plexus that provides innervation to the parenchyma of the liver as well as contributing innervation to some other abdominal structures.
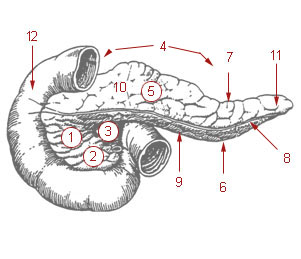
The uncinate process is a small part of the pancreas. The uncinate process is the formed prolongation of the angle of junction of the lower and left lateral borders in the head of the pancreas. The word "uncinate" comes from the Latin "uncinatus", meaning "hooked".

The anterior vagal trunk is one of the two divisions into which the vagus nerve splits as it passes through the esophageal hiatus to enter the abdominal cavity. The anterior and posterior vagal trunks represent the inferior continuation of the esophageal nervous plexus inferior to the diaphragm. The majority of nerve fibres in the anterior vagal trunk are derived from the left vagus nerve.