A testicle or testis is the male gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testicles are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone.

The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein that receives venous return from the upper half of the body, above the diaphragm. Venous return from the lower half, below the diaphragm, flows through the inferior vena cava. The SVC is located in the anterior right superior mediastinum. It is the typical site of central venous access via a central venous catheter or a peripherally inserted central catheter. Mentions of "the cava" without further specification usually refer to the SVC.

In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. The thoracic duct usually begins from the upper aspect of the cisterna chyli, passing out of the abdomen through the aortic hiatus into first the posterior mediastinum and then the superior mediastinum, extending as high up as the root of the neck before descending to drain into the systemic (blood) circulation at the venous angle.

The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body, which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males.

The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest.

The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
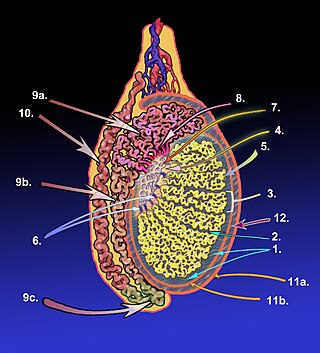
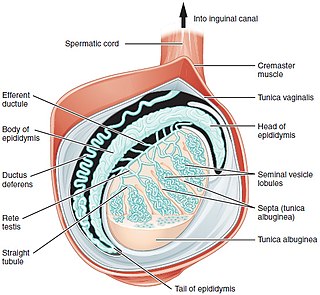
The tunica albugine is a dense, blue-white layer of fibrous tissue surrounding the testis. It is the middle of three enveloppes forming the capsule of the testis; it is deep to the visceral layer of tunica vaginalis, and superficial to the tunica vasculosa testis.

The retropharyngeal space is a potential space and deep compartment of the head and neck situated posterior to the pharynx. The RPS is bounded anteriorly by the buccopharyngeal fascia, posteriorly by the alar fascia, and laterally by the carotid sheath. It extends between the base of the skull superiorly, and the mediastinum inferiorly. It contains the retropharyngeal lymph nodes. Its function is to facilitate movements in the superoinferior axis of the larynx, pharynx, and esophagus in relation to the cervical spine.
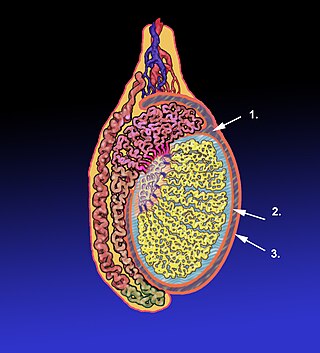
The tunica vaginalis is a pouch of serous membrane within the scrotum that lines the testis and epididymis, and the inner surface of the scrotum. It is the outermost of the three layers that constitute the capsule of the testis, with the tunica albuginea of penis situated beneath it.

The testicular artery is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testicle. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testicles.

The testicular vein, the male gonadal vein, carries deoxygenated blood from its corresponding testis to the inferior vena cava or one of its tributaries. It is the male equivalent of the ovarian vein, and is the venous counterpart of the testicular artery.

The tracheobronchial lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are located around the division of trachea and main bronchi.

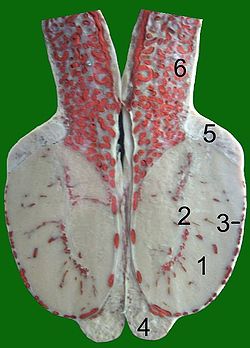
The lobules of testis are of partitions of the testis formed by septa of testis. The lobules of testis contain the tightly coiled seminiferous tubule. There are some hundreds of lobules in a testicle.

The septa testis are fibrous partitions of the testis dividing the testis into compartments - the lobules of the testis. The septa are formed by extensions of the tunica albuginea - the dense fibrous connective tissue surface covering of the testis - into the substance of the testis. The septa converge towards the mediastinum testis.
The tunica albuginea is a layer of condensed fibrous tissue on the surface of the ovary.
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the urogenital or genitourinary system.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

In human male anatomy, the septum of the penis or penile septum refers to the fibrous junction (septum) between the two corpora cavernosa of the human penis. The tunica albuginea of the penis forms a thick fibrous coat to the spongy tissue of the corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum. The two corpora cavernosa are surrounded by a strong fibrous envelope consisting of superficial and deep fibers. The superficial or outer fibers are longitudinal in direction, and form a single tube which encloses both corpora; the deep or inner fibers are arranged circularly around each corpus and meet in the center. By their junction in the median plane, the inner fibers form the intercavernous septum of the penis.
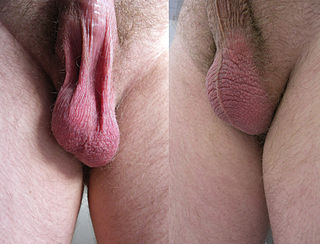
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans, the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of an impact.

Scrotalultrasound is a medical ultrasound examination of the scrotum. It is used in the evaluation of testicular pain, and can help identify solid masses.