Related Research Articles

A spermatozoon is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote.

Fertilisation or fertilization, also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Processes such as insemination or pollination which happen before the fusion of gametes are also sometimes informally called fertilisation. The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction. During double fertilisation in angiosperms the haploid male gamete combines with two haploid polar nuclei to form a triploid primary endosperm nucleus by the process of vegetative fertilisation.

Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare exceptions the fetus is unable to survive.
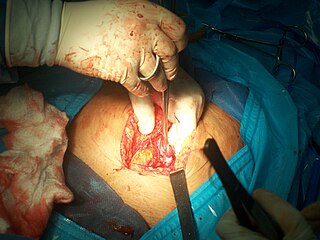
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure for female sterilization in which the fallopian tubes are permanently blocked, clipped or removed. This prevents the fertilization of eggs by sperm and thus the implantation of a fertilized egg. Tubal ligation is considered a permanent method of sterilization and birth control.

Intracytoplasmic sperm injection is an in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in which a single sperm cell is injected directly into the cytoplasm of an egg. This technique is used in order to prepare the gametes for the obtention of embryos that may be transferred to a maternal uterus. With this method, the acrosome reaction is skipped.

The epididymis is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system. It is present in all male reptiles, birds, and mammals. It is a single, narrow, tightly-coiled tube in adult humans, 6 to 7 meters in length connecting the efferent ducts from the rear of each testicle to its vas deferens.

During fertilization, a sperm must first fuse with the plasma membrane and then penetrate the female egg cell to fertilize it. Fusing to the egg cell usually causes little problem, whereas penetrating through the egg's hard shell or extracellular matrix can be more difficult. Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as the acrosome reaction, which is the reaction that occurs in the acrosome of the sperm as it approaches the egg. The acrosome is a cap-like structure over the anterior half of the sperm's head.

Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubules. These cells are called spermatogonial stem cells. The mitotic division of these produces two types of cells. Type A cells replenish the stem cells, and type B cells differentiate into primary spermatocytes. The primary spermatocyte divides meiotically into two secondary spermatocytes; each secondary spermatocyte divides into two equal haploid spermatids by Meiosis II. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm) by the process of spermiogenesis. These develop into mature spermatozoa, also known as sperm cells. Thus, the primary spermatocyte gives rise to two cells, the secondary spermatocytes, and the two secondary spermatocytes by their subdivision produce four spermatozoa and four haploid cells.
Capacitation is the penultimate step in the maturation of mammalian spermatozoa and is required to render them competent to fertilize an oocyte. This step is a biochemical event; the sperm move normally and look mature prior to capacitation. In vivo, capacitation occurs after ejaculation, when the spermatozoa leave the vagina and enter the superior female reproductive tract. The uterus aids in the steps of capacitation by secreting sterol-binding albumin, lipoproteins, and proteolytic and glycosidasic enzymes such as heparin.
Hyperactivation is a type of sperm motility. Hyperactivated sperm motility is characterised by a high amplitude, asymmetrical beating pattern of the sperm tail (flagellum). This type of motility may aid in sperm penetration of the zona pellucida, which encloses the ovum.

The human reproductive system includes the male reproductive system which functions to produce and deposit sperm; and the female reproductive system which functions to produce egg cells, and to protect and nourish the fetus until birth. Humans have a high level of sexual differentiation. In addition to differences in nearly every reproductive organ, there are numerous differences in typical secondary sex characteristics.

Human reproduction is sexual reproduction that results in human fertilization to produce a human offspring. It typically involves sexual intercourse between a sexually mature person with testes and a sexually mature person with ovaries. During sexual intercourse, the interaction between the reproductive systems in people with testes and people with ovaries results in fertilization of the ovum by the sperm to form a zygote. These specialized reproductive cells are called gametes, which are created in a process called gametogenesis. While normal cells contain 46 chromosomes, gamete cells only contain 23 single chromosomes, and it is when these two cells merge into one zygote cell that genetic recombination occurs and the new zygote contains 23 chromosomes from each parent, giving them 46 chromosomes. The zygote then undergoes a defined development process that is known as human embryogenesis, and this starts the typical 9-month gestation period that is followed by childbirth. The fertilization of the ovum may be achieved by artificial insemination methods, which do not involve sexual intercourse. Assisted reproductive technology also exists.

A hydrosalpinx is a condition that occurs when a Fallopian tube is blocked and fills with serous or clear fluid near the ovary. The blocked tube may become substantially distended giving the tube a characteristic sausage-like or retort-like shape. The condition is often bilateral and the affected tubes may reach several centimeters in diameter. The blocked tubes cause infertility. A Fallopian tube filled with blood is a hematosalpinx, and with pus a pyosalpinx.

A semen analysis, also called seminogram or spermiogram, evaluates certain characteristics of a male's semen and the sperm contained therein. It is done to help evaluate male fertility, whether for those seeking pregnancy or verifying the success of vasectomy. Depending on the measurement method, just a few characteristics may be evaluated or many characteristics may be evaluated. Collection techniques and precise measurement method may influence results.

Fallopian tube obstruction is a major cause of female infertility. Blocked fallopian tubes are unable to let the ovum and the sperm converge, thus making fertilization impossible. Fallopian tubes are also known as oviducts, uterine tubes, and salpinges.

VEZT is a gene located on chromosome 12 and encodes for the protein vezatin. Vezatin is a major component of the cadherin-catenin complex that is critical to the formation and maintenance of adherens junctions. The protein is expressed in most epithelial cells and is crucial to the formation of cell-cell contact junctions. Mutations of the gene can lead to upregulation or downregulation of the protein which can have detrimental effects on physiological systems, particularly those involved in development.

The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges, are paired tubes that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries, in the human female reproductive system. In other mammals they are only called oviducts.

An interstitial pregnancy is a uterine but ectopic pregnancy; the pregnancy is located outside the uterine cavity in that part of the fallopian tube that penetrates the muscular layer of the uterus. The term cornual pregnancy is sometimes used as a synonym, but remains ambiguous as it is also applied to indicate the presence of a pregnancy located within the cavity in one of the two upper "horns" of a bicornuate uterus. Interstitial pregnancies have a higher mortality than ectopics in general.

Hysterosalpingography (HSG), also known as uterosalpingography, is a radiologic procedure to investigate the shape of the uterine cavity and the shape and patency of the Fallopian tubes. It is a special x-ray using dye to look at the womb (uterus) and Fallopian tubes It injects a radio-opaque material into the cervical canal and usually fluoroscopy with image intensification. A normal result shows the filling of the uterine cavity and the bilateral filling of the Fallopian tube with the injection material. To demonstrate tubal rupture, spillage of the material into the peritoneal cavity needs to be observed. It has vital role in treatment of infertility especially in case of fallopian tube blockage.
Chromopertubation is a method for the study of fallopian tube patency for suspected infertility in women caused by fallopian tube obstruction. Occlusion or pathology of the fallopian tubes is the most common cause of suspected infertility. Chromopertubation is sometimes commonly referred to a "laparoscopy and dye" test. It is currently one of the standard procedures in this field. In most cases, chromopertubation is performed to assess and determine the cause of someone's difficulties in getting pregnant.
References
- 1 2 Nakanishi, T.; Isotani, A.; Yamaguchi, R.; Ikawa, M.; Baba, T.; Suarez, S.; Okabe, M. (Sep 2004). "Selective passage through the uterotubal junction of sperm from a mixed population produced by chimeras of calmegin-knockout and wild-type male mice" (Free full text). Biology of Reproduction. 71 (3): 959–965. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.028647 . ISSN 0006-3363. PMID 15151931.
- ↑ Krzanowska, H (1974). "The Passage of Abnormal Spermatozoa Through the Uterotubal Junction of the Mouse". Reproduction. 38 (1): 81–90. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0380081 . PMID 4841384.