| External sphincter muscle of female urethra | |
|---|---|
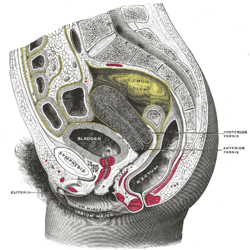 Sagittal section of the lower part of a female trunk, right segment. (Sphincter not labeled) | |
 Muscles of the female perineum. (Urethral sphincter not labeled) | |
| Details | |
| Nerve | Somatic fibers from S2-S4 through pudendal nerve |
| Actions | Constricts urethra and vagina, maintains urinary continence |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus sphincter urethrae externus urethrae femininae |
| TA98 | A09.2.03.006F |
| TA2 | 2422 |
| FMA | 19778 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The external sphincter muscle of the female urethra is a muscle which controls urination in females. The muscle fibers arise on either side from the margin of the inferior ramus of the pubis. They are directed across the pubic arch in front of the urethra, and pass around it to blend with the muscular fibers of the opposite side, between the urethra and vagina.
Contents
The term "urethrovaginal sphincter" ("sphincter urethrovaginalis") is sometimes used to describe the component adjacent to the vagina. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
The "compressor urethrae" is also considered a distinct, adjacent muscle by some sources, [6] [7] [8] [9]