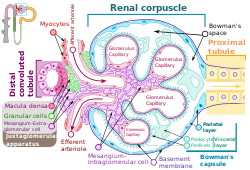
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the foot processes of the podocytes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged ; first with the interstitial fluid outside the tubules, and then into the plasma in the adjacent peritubular capillaries through the endothelial cells lining that capillary. This process regulates the volume of body fluid as well as levels of many body substances. At the end of the tubule, the remaining fluid—urine—exits: it is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.

Smooth (soft) 'muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the other being skeletal and cardiac muscle. Nonetheless, it is found in invertebrates as well and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non-striated, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations. It can be divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multi-unit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium.

The juxtaglomerular apparatus is a structure in the kidney that regulates the function of each nephron, the functional units of the kidney. The juxtaglomerular apparatus is named because it is next to (juxta-) the glomerulus.

Bowman's capsule is a cup-like sac at the beginning of the tubular component of a nephron in the mammalian kidney that performs the first step in the filtration of blood to form urine. A glomerulus is enclosed in the sac. Fluids from blood in the glomerulus are collected in the Bowman's capsule.

Renal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance of toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D.

A renal corpuscle is the blood-filtering component of the nephron of the kidney. It consists of a glomerulus - a tuft of capillaries composed of endothelial cells, and a glomerular capsule known as Bowman's capsule.

The glomerulus is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney. Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium, composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells. The blood is filtered across the capillary walls of this tuft through the glomerular filtration barrier, which yields its filtrate of water and soluble substances to a cup-like sac known as Bowman's capsule. The filtrate then enters the renal tubule of the nephron.

In the kidney, the macula densa is an area of closely packed specialized cells lining the wall of the distal tubule where it touches the glomerulus. Specifically, the macula densa is found in the terminal portion of the distal straight tubule, after which the distal convoluted tubule begins.
Mesangial cells are specialised cells in the kidney that make up the mesangium of the glomerulus. Together with the mesangial matrix, they form the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle. The mesangial cell population accounts for approximately 30-40% of the total cells in the glomerulus. Mesangial cells can be categorized as either extraglomerular mesangial cells or intraglomerular mesangial cells, based on their relative location to the glomerulus. The extraglomerular mesangial cells are found between the afferent and efferent arterioles towards the vascular pole of the glomerulus. The extraglomerular mesangial cells are adjacent to the intraglomerular mesangial cells that are located inside the glomerulus and in between the capillaries. The primary function of mesangial cells is to remove trapped residues and aggregated protein from the basement membrane thus keeping the filter free of debris. The contractile properties of mesangial cells have been shown to be insignificant in changing the filtration pressure of the glomerulus.

Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus. Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. Bowman's capsule filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins while smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars are filtered as the first step in the formation of urine. Although various viscera have epithelial layers, the name visceral epithelial cells usually refers specifically to podocytes, which are specialized epithelial cells that reside in the visceral layer of the capsule.
The basal lamina is a layer of extracellular matrix secreted by the epithelial cells, on which the epithelium sits. It is often incorrectly referred to as the basement membrane, though it does constitute a portion of the basement membrane. The basal lamina is visible only with the electron microscope, where it appears as an electron-dense layer that is 20–100 nm thick.
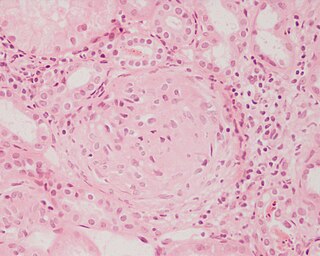
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases. Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or of the small blood vessels in the kidneys, hence the name, but not all diseases necessarily have an inflammatory component.

The basement membrane, also known as base membrane, is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue.

Diabetic nephropathy, also known as diabetic kidney disease, is the chronic loss of kidney function occurring in those with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic nephropathy is the leading causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) globally. The triad of protein leaking into the urine, rising blood pressure with hypertension and then falling renal function is common to many forms of CKD. Protein loss in the urine due to damage of the glomeruli may become massive, and cause a low serum albumin with resulting generalized body swelling (edema) so called nephrotic syndrome. Likewise, the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) may progressively fall from a normal of over 90 ml/min/1.73m2 to less than 15, at which point the patient is said to have end-stage renal disease. It usually is slowly progressive over years.

Hypertensive kidney disease is a medical condition referring to damage to the kidney due to chronic high blood pressure. It manifests as hypertensive nephrosclerosis. It should be distinguished from renovascular hypertension, which is a form of secondary hypertension, and thus has opposite direction of causation.

In the renal system, peritubular capillaries are tiny blood vessels, supplied by the efferent arteriole, that travel alongside nephrons allowing reabsorption and secretion between blood and the inner lumen of the nephron. Peritubular capillaries surround the cortical parts of the proximal and distal tubules, while the vasa recta go into the medulla to approach the loop of Henle.
In the physiology of the kidney, tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF) is a feedback system inside the kidneys. Within each nephron, information from the renal tubules is signaled to the glomerulus. Tubuloglomerular feedback is one of several mechanisms the kidney uses to regulate glomerular filtration rate (GFR). It involves the concept of purinergic signaling, in which an increased distal tubular sodium chloride concentration causes a basolateral release of adenosine from the macula densa cells. This initiates a cascade of events that ultimately brings GFR to an appropriate level.
The myogenic mechanism is how arteries and arterioles react to an increase or decrease of blood pressure to keep the blood flow constant within the blood vessel. Myogenic response refers to a contraction initiated by the myocyte itself instead of an outside occurrence or stimulus such as nerve innervation. Most often observed in smaller resistance arteries, this 'basal' myogenic tone may be useful in the regulation of organ blood flow and peripheral resistance, as it positions a vessel in a preconstricted state that allows other factors to induce additional constriction or dilation to increase or decrease blood flow.

Extraglomerular mesangial cells are light-staining pericytes in the kidney found outside the glomerulus, near the vascular pole. They resemble smooth muscle cells and play a role in renal autoregulation of blood flow to the kidney and regulation of systemic blood pressure through the renin–angiotensin system. Extraglomerular mesangial cells are part of the juxtaglomerular apparatus, along with the macula densa cells of the distal convoluted tubule and the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent arteriole.

The glomerular basement membrane of the kidney is the basal lamina layer of the glomerulus. The glomerular endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane, and the filtration slits between the podocytes perform the filtration function of the glomerulus, separating the blood in the capillaries from the filtrate that forms in Bowman's capsule. The glomerular basement membrane is a fusion of the endothelial cell and podocyte basal laminas, and is the main site of restriction of water flow. Glomerular basement membrane is secreted and maintained by podocyte cells.