
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about 12 centimetres in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder.

The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled through the urethra during urination. The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra.
The excretory system is a passive biological system that removes excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. The dual function of excretory systems is the elimination of the waste products of metabolism and to drain the body of used up and broken down components in a liquid and gaseous state. In humans and other amniotes, most of these substances leave the body as urine and to some degree exhalation, mammals also expel them through sweating.

The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lined with urothelial cells, a form of transitional epithelium, and feature an extra layer of smooth muscle in the lower third to aid in peristalsis. The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone. Stenosis is when a ureter is narrowed, due to for example chronic inflammation. Congenital abnormalities that affect the ureters can include the development of two ureters on the same side or abnormally placed ureters. Additionally, reflux of urine from the bladder back up the ureters is a condition commonly seen in children.

The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space behind (retro) the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal.

The renal calyces are conduits in the kidney through which urine passes. The minor calyces form a cup-shaped drain around the apex of the renal pyramids. Urine formed in the kidney passes through a renal papilla at the apex into the minor calyx; 4-5 minor calyces converge to form a major calyx through which urine passes into the renal pelvis.
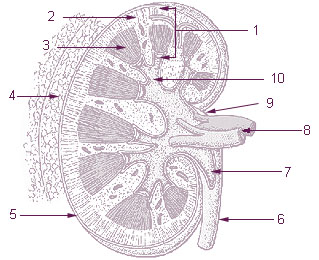
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries which then branch to form interlobar arteries. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, and these finally reach the glomeruli. At the glomerulus the blood reaches a highly disfavourable pressure gradient and a large exchange surface area, which forces the serum portion of the blood out of the vessel and into the renal tubules. Flow continues through the renal tubules, including the proximal tubule, the loop of Henle, through the distal tubule and finally leaves the kidney by means of the collecting duct, leading to the renal pelvis, the dilated portion of the ureter.

The renal pelvis or pelvis of the kidney is the funnel-like dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. It is formed by the convergence of the major calyces, acting as a funnel for urine flowing from the major calyces to the ureter. It has a mucous membrane and is covered with transitional epithelium and an underlying lamina propria of loose-to-dense connective tissue.

The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.
The development of the urinary system begins during prenatal development, and relates to the development of the urogenital system – both the organs of the urinary system and the sex organs of the reproductive system. The development continues as a part of sexual differentiation.

Hydronephrosis describes hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dilation of the entire upper urinary tract.
Horseshoe kidney, also known as ren arcuatus, renal fusion or super kidney, is a congenital disorder affecting about 1 in 500 people that is more common in men, often asymptomatic, and usually diagnosed incidentally. In this disorder, the patient's kidneys fuse to form a horseshoe-shape during development in the womb. The fused part is the isthmus of the horseshoe kidney. The abnormal anatomy can affect kidney drainage resulting in increased frequency of kidney stones and urinary tract infections as well as increase risk of certain renal cancers.

Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), also known as vesicoureteric reflux, is a condition in which urine flows retrograde, or backward, from the bladder into one or both ureters and then to the renal calyx or kidneys. Urine normally travels in one direction from the kidneys to the bladder via the ureters, with a one-way valve at the vesicoureteral (ureteral-bladder) junction preventing backflow. The valve is formed by oblique tunneling of the distal ureter through the wall of the bladder, creating a short length of ureter (1–2 cm) that can be compressed as the bladder fills. Reflux occurs if the ureter enters the bladder without sufficient tunneling, i.e., too "end-on".
Kidney development, or nephrogenesis, describes the embryologic origins of the kidney, a major organ in the urinary system. This article covers a 3 part developmental process that is observed in most reptiles, birds and mammals, including humans. Nephrogenesis is often considered in the broader context of the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
The metanephrogenic blastema or metanephric blastema is one of the two embryological structures that give rise to the kidney, the other being the ureteric bud.
Pyelogram is a form of imaging of the renal pelvis and ureter.

The renal hylus or renal pedicle is the hylus of the kidney, that is, its recessed central fissure where its vessels, nerves and ureter pass. The medial border of the kidney is concave in the center and convex toward either extremity; it is directed forward and a little downward. Its central part presents a deep longitudinal fissure, bounded by prominent overhanging anterior and posterior lips. This fissure is a hylus that transmits the vessels, nerves, and ureter. From anterior to posterior, the renal vein exits, the renal artery enters, and the renal pelvis exits the kidney.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a minimally-invasive procedure to remove stones from the kidney by a small puncture wound through the skin. It is most suitable to remove stones of more than 2 cm in size and which are present near the pelvic region. It is usually done under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia.

Fraley syndrome is a condition where the superior infundibulum of the upper calyx of the kidney is obstructed by the crossing renal artery branch, causing distension and dilatation of the calyx and presenting clinically as haematuria and nephralgia. Furthermore, when the renal artery obstructs the proximal collecting system, filling defects can occur anywhere in the calyces, pelvis, or ureter.

Renal ultrasonography is the examination of one or both kidneys using medical ultrasound.











