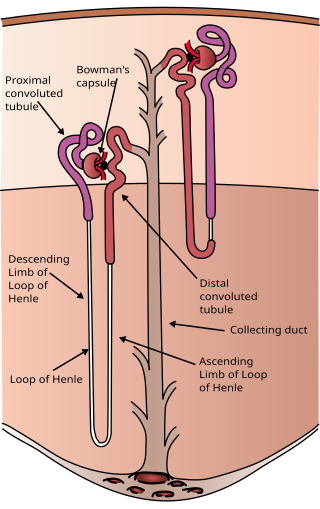
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the podocyte foot processes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged ; first with the interstitial fluid outside the tubules, and then into the plasma in the adjacent peritubular capillaries through the endothelial cells lining that capillary. This process regulates the volume of body fluid as well as levels of many body substances. At the end of the tubule, the remaining fluid—urine—exits: it is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.

Bowman's capsule is a cup-like sac at the beginning of the tubular component of a nephron in the mammalian kidney that performs the first step in the filtration of blood to form urine. A glomerulus is enclosed in the sac. Fluids from blood in the glomerulus are collected in the Bowman's capsule.

A renal corpuscle is the blood-filtering component of the nephron of the kidney. It consists of a glomerulus - a tuft of capillaries composed of endothelial cells - and a glomerular capsule known as Bowman's capsule.

The glomerulus is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney. Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium, composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells. The blood is filtered across the capillary walls of this tuft through the glomerular filtration barrier, which yields its filtrate of water and soluble substances to a cup-like sac known as Bowman's capsule. The filtrate then enters the renal tubule of the nephron.

Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder affecting around 1 in 5,000–10,000 children, characterized by glomerulonephritis, end-stage kidney disease, and hearing loss. Alport syndrome can also affect the eyes, though the changes do not usually affect vision, except when changes to the lens occur in later life. Blood in urine is universal. Proteinuria is a feature as kidney disease progresses.
Mesangial cells are specialised cells in the kidney that make up the mesangium of the glomerulus. Together with the mesangial matrix, they form the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle. The mesangial cell population accounts for approximately 30-40% of the total cells in the glomerulus. Mesangial cells can be categorized as either extraglomerular mesangial cells or intraglomerular mesangial cells, based on their relative location to the glomerulus. The extraglomerular mesangial cells are found between the afferent and efferent arterioles towards the vascular pole of the glomerulus. The extraglomerular mesangial cells are adjacent to the intraglomerular mesangial cells that are located inside the glomerulus and in between the capillaries. The primary function of mesangial cells is to remove trapped residues and aggregated protein from the basement membrane thus keeping the filter free of debris. The contractile properties of mesangial cells have been shown to be insignificant in changing the filtration pressure of the glomerulus.

Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus. Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. Bowman's capsule filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins while smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars are filtered as the first step in the formation of urine. Although various viscera have epithelial layers, the name visceral epithelial cells usually refers specifically to podocytes, which are specialized epithelial cells that reside in the visceral layer of the capsule.

Goodpasture syndrome (GPS), also known as anti–glomerular basement membrane disease, is a rare autoimmune disease in which antibodies attack the basement membrane in lungs and kidneys, leading to bleeding from the lungs, glomerulonephritis, and kidney failure. It is thought to attack the alpha-3 subunit of type IV collagen, which has therefore been referred to as Goodpasture's antigen. Goodpasture syndrome may quickly result in permanent lung and kidney damage, often leading to death. It is treated with medications that suppress the immune system such as corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide, and with plasmapheresis, in which the antibodies are removed from the blood.
The basal lamina is a layer of extracellular matrix secreted by the epithelial cells, on which the epithelium sits. It is often incorrectly referred to as the basement membrane, though it does constitute a portion of the basement membrane. The basal lamina is visible only with the electron microscope, where it appears as an electron-dense layer that is 20–100 nm thick.
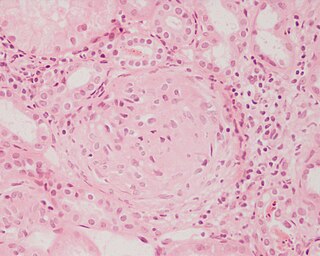
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases. Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or of the small blood vessels in the kidneys, hence the name, but not all diseases necessarily have an inflammatory component.

The basement membrane, also known as base membrane, is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue.

Diabetic nephropathy, also known as diabetic kidney disease, is the chronic loss of kidney function occurring in those with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic nephropathy is the leading causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) globally. The triad of protein leaking into the urine, rising blood pressure with hypertension and then falling renal function is common to many forms of CKD. Protein loss in the urine due to damage of the glomeruli may become massive, and cause a low serum albumin with resulting generalized body swelling (edema) so called nephrotic syndrome. Likewise, the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) may progressively fall from a normal of over 90 ml/min/1.73m2 to less than 15, at which point the patient is said to have end-stage renal disease. It usually is slowly progressive over years.

Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a histopathologic finding of scarring (sclerosis) of glomeruli and damage to renal podocytes. This process damages the filtration function of the kidney, resulting in protein presence in the urine due to protein loss. FSGS is a leading cause of excess protein loss—nephrotic syndrome—in children and adults in the US. Signs and symptoms include proteinuria and edema. Kidney failure is a common long-term complication of the disease. FSGS can be classified as primary, secondary, or genetic, depending on whether a particular toxic or pathologic stressor or genetic predisposition can be identified as the cause. Diagnosis is established by renal biopsy, and treatment consists of glucocorticoids and other immune-modulatory drugs. Response to therapy is variable, with a significant portion of patients progressing to end-stage kidney failure. An American epidemiological study 20 years ago demonstrated that FSGS is estimated to occur in 7 persons per million, with cisgender male African-Americans at higher risk.

Intraglomerular mesangial cells are mesangial cells located among the glomerular capillaries within a renal corpuscle of a kidney.

Nephrin is a protein necessary for the proper functioning of the renal filtration barrier. The renal filtration barrier consists of fenestrated endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane, and the podocytes of epithelial cells. Nephrin is a transmembrane protein that is a structural component of the slit diaphragm. It is present on the tips of the podocytes as an intricate mesh connecting adjacent foot processes. Nephrin contributes to the strong size selectivity of the slit diaphragm, however, the relative contribution of the slit diaphragm to exclusion of protein by the glomerulus is debated. The extracellular interactions, both homophilic and heterophilic—between nephrin and NEPH1—are not completely understood. In addition to eight immunoglobulin G–like motifs and a fibronectin type 3 repeat, nephrin has a single transmembrane domain and a short intracellular tail. Tyrosine phosphorylation at different sites on the intracellular tail contribute to the regulation of slit diaphragm formation during development and repair in pathology affecting podocytes. Podocin may interact with nephrin to guide it onto lipid rafts in podocytes, requiring the integrity of an arginine residue of nephrin at position 1160.

In renal physiology, ultrafiltration occurs at the barrier between the blood and the filtrate in the glomerular capsule in the kidneys. As in nonbiological examples of ultrafiltration, pressure and concentration gradients lead to a separation through a semipermeable membrane. The Bowman's capsule contains a dense capillary network called the glomerulus. Blood flows into these capillaries through the afferent arterioles and leaves through the efferent arterioles.
Podocin is a protein component of the filtration slits of podocytes. Glomerular capillary endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane and the filtration slits function as the filtration barrier of the kidney glomerulus. Mutations in the podocin gene NPHS2 can cause nephrotic syndrome, such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) or minimal change disease (MCD). Symptoms may develop in the first few months of life or later in childhood.
Collagen IV is a type of collagen found primarily in the basal lamina. The collagen IV C4 domain at the C-terminus is not removed in post-translational processing, and the fibers link head-to-head, rather than in parallel. Also, collagen IV lacks the regular glycine in every third residue necessary for the tight, collagen helix. This makes the overall arrangement more sloppy with kinks. These two features cause the collagen to form in a sheet, the form of the basal lamina. Collagen IV is the more common usage, as opposed to the older terminology of "type-IV collagen". Collagen IV exists in all metazoan phyla, to whom they served as an evolutionary stepping stone to multicellularity.

Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 or Transient receptor potential canonical 6, also known as TRPC6, is a protein encoded in the human by the TRPC6 gene. TRPC6 is a transient receptor potential channel of the classical TRPC subfamily.

Foot processes are specialized protrusive cellular extensions that may exhibit a pyramidal or finger-like morphology. They are most evident in mural cells, that are associated with and ensheath walls of blood capillaries, such as pericytes, podocytes and astrocytes.
















