
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into organology, the study of organs, histology, the study of tissues, and cytology, the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms.

The proximal tubule is the segment of the nephron in kidneys which begins from the renal pole of the Bowman's capsule to the beginning of loop of Henle. At this location, the glomerular parietal epithelial cells (PECs) lining bowman’s capsule abruptly transition to proximal tubule epithelial cells (PTECs). The proximal tubule can be further classified into the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and the proximal straight tubule (PST).

The renal calyces are conduits in the kidney through which urine passes. The minor calyces form a cup-shaped drain around the apex of the renal pyramids. Urine formed in the kidney passes through a renal papilla at the apex into the minor calyx; 4-5 minor calyces converge to form a major calyx through which urine passes into the renal pelvis.
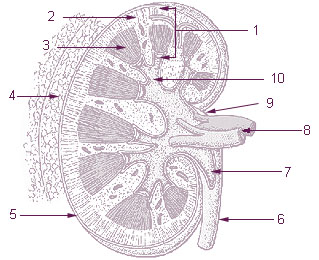
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries which then branch to form interlobar arteries. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, and these finally reach the glomeruli. At the glomerulus the blood reaches a highly disfavourable pressure gradient and a large exchange surface area, which forces the serum portion of the blood out of the vessel and into the renal tubules. Flow continues through the renal tubules, including the proximal tubule, the loop of Henle, through the distal tubule and finally leaves the kidney by means of the collecting duct, leading to the renal pelvis, the dilated portion of the ureter.
The basal lamina is a layer of extracellular matrix secreted by the epithelial cells, on which the epithelium sits. It is often incorrectly referred to as the basement membrane, though it does constitute a portion of the basement membrane. The basal lamina is visible only with the electron microscope, where it appears as an electron-dense layer that is 20–100 nm thick.
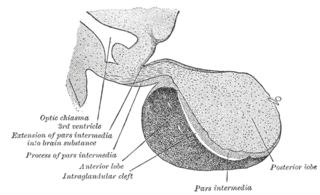
Pars intermedia is the boundary between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary. It contains colloid-filled cysts and two types of cells - basophils and chromophobes. The cysts are the remainder of Rathke’s pouch. As technically part of the anterior pituitary, it separates the posterior pituitary and pars distalis. It is composed of large, pale cells that encompass the aforementioned colloid-filled follicles.
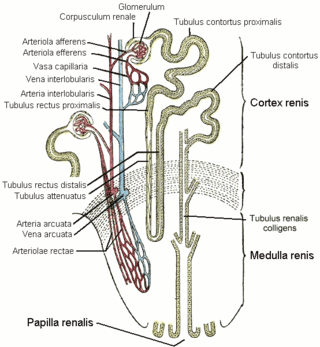
The vasa recta of the kidney, are the straight arterioles, and the straight venules of the kidney, – a series of blood vessels in the blood supply of the kidney that enter the medulla as the straight arterioles, and leave the medulla to ascend to the cortex as the straight venules.. They lie parallel to the loop of Henle.

In the renal system, peritubular capillaries are tiny blood vessels, supplied by the efferent arteriole, that travel alongside nephrons allowing reabsorption and secretion between blood and the inner lumen of the nephron. Peritubular capillaries surround the cortical parts of the proximal and distal tubules, while the vasa recta go into the medulla to approach the loop of Henle.

The lamina muscularis mucosae is a thin layer of muscle of the gastrointestinal tract, located outside the lamina propria, and separating it from the submucosa. It is present in a continuous fashion from the esophagus to the upper rectum. A discontinuous muscularis mucosae–like muscle layer is present in the urinary tract, from the renal pelvis to the bladder; as it is discontinuous, it should not be regarded as a true muscularis mucosae.

Cortical radial arteries, formerly known as interlobular arteries, are renal blood vessels given off at right angles from the side of the arcuate arteries looking toward the cortical substance. The interlobular arteries pass directly outward between the medullary rays to reach the fibrous tunic, where they end in the capillary network of this part.
A cortical lobule is a part of a renal lobe. It consists of the nephrons grouped around a single medullary ray, and draining into a single collecting duct. Its near identical parallel is the rectal lobe, which is present in the majority of mammals.

The arcuate arteries of the kidney, also known as arciform arteries, are vessels of the renal circulation. They are located at the border of the renal cortex and renal medulla.

The arcuate vein is a vessel of the renal circulation. It is located at the border of the renal cortex and renal medulla. Arcuate veins pass around the renal pyramids at the border between the renal cortex and renal medulla in an arch shape. Arcuate veins receive blood from cortical radiate veins, and in turn deliver blood into the arcuate veins.

The interlobar arteries are vessels of the renal circulation which supply the renal lobes. The interlobar arteries branch from the lobar arteries which branch from the segmental arteries, from the renal artery. They give rise to arcuate arteries.

The interlobar veins are veins of the renal circulation which drain the renal lobes. They collect blood from the arcuate veins. The interlobar veins unite to form a renal vein. Each interlobar vein passes along the edge of the renal pyramids.

Within the nephron of the kidney, the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is a segment of the heterogenous loop of Henle downstream of the descending limb, after the sharp bend of the loop. This part of the renal tubule is divided into a thin and thick ascending limb; the thick portion is also known as the distal straight tubule, in contrast with the distal convoluted tubule downstream.

A chromophobe is a histological structure that does not stain readily, and thus appears relatively pale under the microscope.

In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension of an organ that can be determined without the use of a microscope at the gross anatomy level. This is in contrast to the much smaller lobule, which is a clear division only visible under the microscope.
In anatomy, a medullary ray is the middle part of a cortical lobule. Each consists of a group of nephrons in the renal cortex. Their name is potentially misleading, as "medullary" refers to their destination, not their location. They travel perpendicular to the capsule, and extend from the cortex to the medulla. They may be visualised during urography.
The transmission electron microscope (TEM) is used as an important diagnostic tool to screen human tissues at high magnification, often in conjunction with other methods, particularly light microscopy and immunofluorescence techniques. The TEM was first used extensively for this purpose in the 1980s, especially for identifying the markers of cell differentiation to identify tumours, and in renal disease. Immunolabelling techniques are now generally used instead of the TEM for tumour diagnosis but the technique retains a critical role in the diagnosis of renal disease and a range of other conditions.












