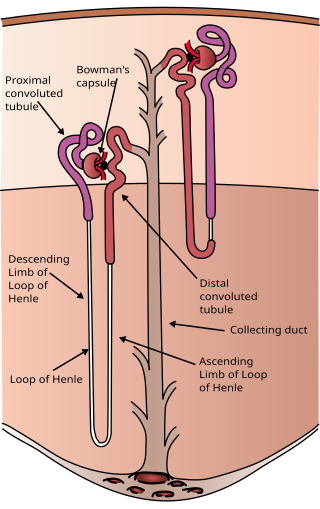
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the foot processes of the podocytes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged ; first with the interstitial fluid outside the tubules, and then into the plasma in the adjacent peritubular capillaries through the endothelial cells lining that capillary. This process regulates the volume of body fluid as well as levels of many body substances. At the end of the tubule, the remaining fluid—urine—exits: it is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.

Renal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance of toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D.

The proximal tubule is the segment of the nephron in kidneys which begins from the renal pole of the Bowman's capsule to the beginning of loop of Henle. At this location, the glomerular parietal epithelial cells (PECs) lining bowman’s capsule abruptly transition to proximal tubule epithelial cells (PTECs). The proximal tubule can be further classified into the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and the proximal straight tubule (PST).

In the kidney, the loop of Henle is the portion of a nephron that leads from the proximal convoluted tubule to the distal convoluted tubule. Named after its discoverer, the German anatomist Friedrich Gustav Jakob Henle, the loop of Henle's main function is to create a concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney.

Loop diuretics are pharmacological agents that primarily inhibit the Na-K-Cl cotransporter located on the luminal membrane of cells along the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. They are often used for the treatment of hypertension and edema secondary to congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, or chronic kidney disease. While thiazide diuretics are more effective in patients with normal kidney function, loop diuretics are more effective in patients with impaired kidney function.

Thiazide refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The first approved drug of this class, chlorothiazide, was marketed under the trade name Diuril beginning in 1958. In most countries, thiazides are the least expensive antihypertensive drugs available.
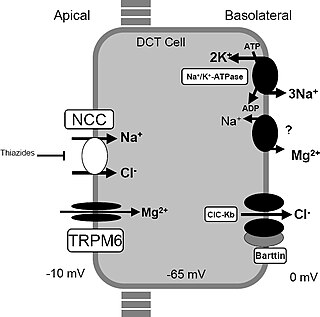
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. It is the most frequent hereditary salt-losing tubulopathy. Gitelman syndrome is caused by disease-causing variants on both alleles of the SLC12A3 gene. The SLC12A3 gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter, which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney.
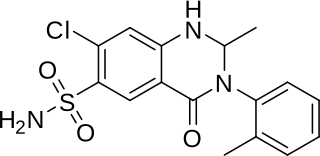
Metolazone is a thiazide-like diuretic marketed under the brand names Zytanix, Metoz, Zaroxolyn, and Mykrox. It is primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure. Metolazone indirectly decreases the amount of water reabsorbed into the bloodstream by the kidney, so that blood volume decreases and urine volume increases. This lowers blood pressure and prevents excess fluid accumulation in heart failure. Metolazone is sometimes used together with loop diuretics such as furosemide or bumetanide, but these highly effective combinations can lead to dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities.

Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare inherited disease characterised by a defect in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which results in low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increased blood pH (alkalosis), and normal to low blood pressure. There are two types of Bartter syndrome: neonatal and classic. A closely associated disorder, Gitelman syndrome, is milder than both subtypes of Bartter syndrome.
In the physiology of the kidney, tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF) is a feedback system inside the kidneys. Within each nephron, information from the renal tubules is signaled to the glomerulus. Tubuloglomerular feedback is one of several mechanisms the kidney uses to regulate glomerular filtration rate (GFR). It involves the concept of purinergic signaling, in which an increased distal tubular sodium chloride concentration causes a basolateral release of adenosine from the macula densa cells. This initiates a cascade of events that ultimately brings GFR to an appropriate level.
Sodium-dependent glucose cotransporters are a family of glucose transporter found in the intestinal mucosa (enterocytes) of the small intestine (SGLT1) and the proximal tubule of the nephron. They contribute to renal glucose reabsorption. In the kidneys, 100% of the filtered glucose in the glomerulus has to be reabsorbed along the nephron. If the plasma glucose concentration is too high (hyperglycemia), glucose passes into the urine (glucosuria) because SGLT are saturated with the filtered glucose.
The Na–K–Cl cotransporter (NKCC) is a transport protein that aids in the secondary active transport of sodium, potassium, and chloride into cells. In humans there are two isoforms of this membrane transport protein, NKCC1 and NKCC2, encoded by two different genes. Two isoforms of the NKCC1/Slc12a2 gene result from keeping or skipping exon 21 in the final gene product.

The sodium-chloride symporter (also known as Na+-Cl− cotransporter, NCC or NCCT, or as the thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl− cotransporter or TSC) is a cotransporter in the kidney which has the function of reabsorbing sodium and chloride ions from the tubular fluid into the cells of the distal convoluted tubule of the nephron. It is a member of the SLC12 cotransporter family of electroneutral cation-coupled chloride cotransporters. In humans, it is encoded by the SLC12A3 gene (solute carrier family 12 member 3) located in 16q13.

Clopamide is a piperidine diuretic.

Within the nephron of the kidney, the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is a segment of the heterogenous loop of Henle downstream of the descending limb, after the sharp bend of the loop. This part of the renal tubule is divided into a thin and thick ascending limb; the thick portion is also known as the distal straight tubule, in contrast with the distal convoluted tubule downstream.

Dent's disease is a rare X-linked recessive inherited condition that affects the proximal renal tubules of the kidney. It is one cause of Fanconi syndrome, and is characterized by tubular proteinuria, excess calcium in the urine, formation of calcium kidney stones, nephrocalcinosis, and chronic kidney failure.

WNK , also known as WNK1, is an enzyme that is encoded by the WNK1 gene. WNK1 is serine-threonine protein kinase and part of the "with no lysine/K" kinase WNK family. The predominant role of WNK1 is the regulation of cation-Cl− cotransporters (CCCs) such as the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), basolateral Na-K-Cl symporter (NKCC1), and potassium chloride cotransporter (KCC1) located within the kidney. CCCs mediate ion homeostasis and modulate blood pressure by transporting ions in and out of the cell. WNK1 mutations as a result have been implicated in blood pressure disorders/diseases; a prime example being familial hyperkalemic hypertension (FHHt).
In renal physiology, renal sodium reabsorption refers to the process by which the kidneys, having filtered out waste products from the blood to be excreted as urine, re-absorb sodium ions (Na2+) from the waste. It uses Na-H antiport, Na-glucose symport, sodium ion channels (minor). It is stimulated by angiotensin II and aldosterone, and inhibited by atrial natriuretic peptide.

Serine/threonine protein kinase WNK4 also known as WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 4 or WNK4, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the WNK4 gene. Missense mutations cause a genetic form of pseudohypoaldosteronism type 2, also called Gordon syndrome.

A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin, is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.