
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters.
Transient receptor potential channels are a group of ion channels located mostly on the plasma membrane of numerous animal cell types. Most of these are grouped into two broad groups: Group 1 includes TRPC, TRPV, TRPVL, TRPM, TRPS, TRPN, and TRPA. Group 2 consists of TRPP and TRPML. Other less-well categorized TRP channels exist, including yeast channels and a number of Group 1 and Group 2 channels present in non-animals. Many of these channels mediate a variety of sensations such as pain, temperature, different kinds of taste, pressure, and vision. In the body, some TRP channels are thought to behave like microscopic thermometers and used in animals to sense hot or cold. Some TRP channels are activated by molecules found in spices like garlic (allicin), chili pepper (capsaicin), wasabi ; others are activated by menthol, camphor, peppermint, and cooling agents; yet others are activated by molecules found in cannabis or stevia. Some act as sensors of osmotic pressure, volume, stretch, and vibration. Most of the channels are activated or inhibited by signaling lipids and contribute to a family of lipid-gated ion channels.
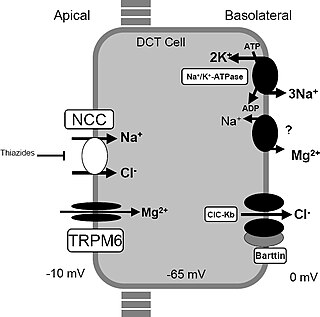
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. It is the most frequent hereditary salt-losing tubulopathy. Gitelman syndrome is caused by disease-causing variants on both alleles of the SLC12A3 gene. The SLC12A3 gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter, which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney.

Klotho is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KL gene. The three subfamilies of klotho are α-klotho, β-klotho, and γ-klotho. α-klotho activates FGF23, and β-klotho activates FGF19 and FGF21. When the subfamily is not specified, the word "klotho" typically refers to the α-klotho subfamily, because α-klotho was discovered before the other members.

TRPV6 is a membrane calcium (Ca2+) channel protein which is particularly involved in the first step in Ca2+absorption in the intestine.
TRPC is a family of transient receptor potential cation channels in animals.
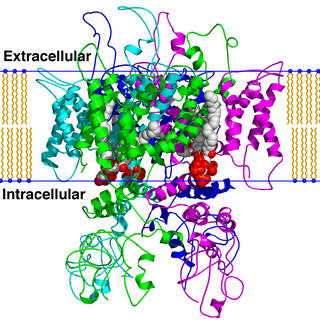
TRPV is a family of transient receptor potential cation channels in animals. All TRPVs are highly calcium selective.
TRPM is a family of transient receptor potential ion channels (M standing for wikt:melastatin). Functional TRPM channels are believed to form tetramers. The TRPM family consists of eight different channels, TRPM1–TRPM8.

Transient receptor potential canonical 1 (TRPC1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPC1 gene.

Short transient receptor potential channel 5 (TrpC5) also known as transient receptor protein 5 (TRP-5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPC5 gene. TrpC5 is subtype of the TRPC family of mammalian transient receptor potential ion channels.

Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 2, also known as TRPM2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPM2 gene.

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 5 (TRPM5), also known as long transient receptor potential channel 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPM5 gene.

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPV2 gene. TRPV2 is a nonspecific cation channel that is a part of the TRP channel family. This channel allows the cell to communicate with its extracellular environment through the transfer of ions, and responds to noxious temperatures greater than 52 °C. It has a structure similar to that of potassium channels, and has similar functions throughout multiple species; recent research has also shown multiple interactions in the human body.

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4 (hTRPM4), also known as melastatin-4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPM4 gene.

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPM3 gene.

Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 7, also known as TRPM7, is a human gene encoding a protein of the same name.

S100 calcium-binding protein A10 (S100A10), also known as p11, is a protein that is encoded by the S100A10 gene in humans and the S100a10 gene in other species. S100A10 is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing two EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells. They regulate a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. The S100 protein is implicated in exocytosis and endocytosis by reorganization of F-actin.

Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor, type 2, also known as ITPR2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ITPR2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is both a receptor for inositol triphosphate and a calcium channel.
The transient receptor potential Ca2+ channel (TRP-CC) family (TC# 1.A.4) is a member of the voltage-gated ion channel (VIC) superfamily and consists of cation channels conserved from worms to humans. The TRP-CC family also consists of seven subfamilies (TRPC, TRPV, TRPM, TRPN, TRPA, TRPP, and TRPML) based on their amino acid sequence homology:
- the canonical or classic TRPs,
- the vanilloid receptor TRPs,
- the melastatin or long TRPs,
- ankyrin (whose only member is the transmembrane protein 1 [TRPA1])
- TRPN after the nonmechanoreceptor potential C (nonpC), and the more distant cousins,
- the polycystins
- and mucolipins.

ZINC17988990 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective inhibitor for the TRPV5 calcium channel, with an IC50 of 177 nM and high selectivity for TRPV5 over TRPV6 and the other subtypes of TRPV. It is the first selective inhibitor to be developed for TRPV5, and may be useful for modulating calcium reabsorption in the kidneys.




















