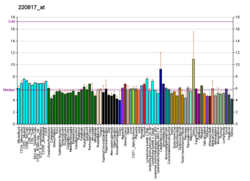
| TRPC4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | TRPC4 , HTRP-4, HTRP4, TRP4, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily C member 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 603651; MGI: 109525; HomoloGene: 22955; GeneCards: TRPC4; OMA:TRPC4 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The short transient receptor potential channel 4 (TrpC4), also known as Trp-related protein 4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPC4 gene. [5] [6]