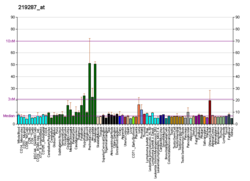
| KCNMB4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | KCNMB4 , potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily M regulatory beta subunit 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 605223; MGI: 1913272; HomoloGene: 8721; GeneCards: KCNMB4; OMA:KCNMB4 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNMB4 gene. [5] [6] [7]
Contents
MaxiK channels are large conductance, voltage and calcium-sensitive potassium channels which are fundamental to the control of smooth muscle tone and neuronal excitability. MaxiK channels can be formed by 2 subunits: the pore-forming alpha subunit and the modulatory beta subunit. The protein encoded by this gene is an auxiliary beta subunit which slows activation kinetics, leads to steeper calcium sensitivity, and shifts the voltage range of current activation to more negative potentials than does the beta 1 subunit. [7]