Calcium-activated potassium channels are potassium channels gated by calcium, or that are structurally or phylogenetically related to calcium gated channels. They were first discovered in 1958 by Gardos who saw that Calcium levels inside of a cell could affect the permeability of potassium through that cell membrane. Then in 1970, Meech was the first to observe that intracellular calcium could trigger potassium currents. In humans they are divided into three subtypes: large conductance or BK channels, which have very high conductance which range from 100 to 300 pS, intermediate conductance or IK channels, with intermediate conductance ranging from 25 to 100 pS, and small conductance or SK channels with small conductances from 2-25 pS.

Kv7.3 (KvLQT3) is a potassium channel protein coded for by the gene KCNQ3.

SK3 also known as KCa2.3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNN3 gene.
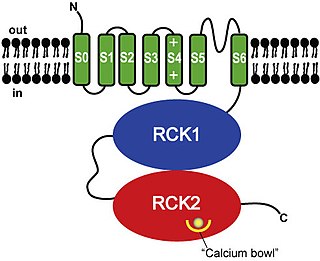
Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit alpha-1 also known as large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel, subfamily M, alpha member 1 (KCa1.1), or BK channel alpha subunit, is a voltage gated potassium channel encoded by the KCNMA1 gene and characterized by their large conductance of potassium ions (K+) through cell membranes.

Potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4, also known as KCNN4, is a human gene encoding the KCa3.1 protein.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK1 gene.

Cav1.1 also known as the calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1S subunit, (CACNA1S), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CACNA1S gene. It is also known as CACNL1A3 and the dihydropyridine receptor.

Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACNB4 gene.

Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNAB1 gene.

Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 15, also known as KCNJ15 is a human gene, which encodes the Kir4.2 protein.
Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNMB2 gene.

Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNMB3 gene.

Potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 2, also known as KCNN2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KCNN2 gene. KCNN2 is an ion channel protein also known as KCa2.2.

Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNQ5 gene.

Potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 1 , also known as KCNN1 is a human gene encoding the KCa2.1 protein.

Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNMB4 gene.

Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 6 also known as Kv1.6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNA6 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a voltage-gated potassium channel subunit.

Potassium channel subfamily T, member 1, also known as KCNT1 is a human gene that encodes the KCa4.1 protein. KCa4.1 is a member of the calcium-activated potassium channel protein family

Potassium channel subfamily T, member 2, also known as KCNT2 is a human gene that encodes the KNa protein. KCNT2, also known as the Slick channel is an outwardly rectifying potassium channel activated by internal raises in sodium or chloride ions.

Lawrence B. Salkoff is an American neuroscientist and currently a professor of neuroscience and genetics at Washington University School of Medicine
Celia M. Santi, Alice Butler, Julia Kuhn, Aguan Wei, Lawrence Salkoff. Bovine and mouse SLO3 K+ channels: Evolutionary divergence points to a RCK1 region of critical function. J Biol Chem.284: 21589-98 (2009).

















