Function
The zona pellucida (ZP) is a specialized extracellular matrix that surrounds the oocyte and early embryo. It is composed of three or four glycoproteins (ZP1-4) with various functions during oogenesis, fertilization and preimplantation development. The protein encoded by this gene is a major structural component of the ZP and functions in primary binding and stimulation of the sperm acrosome reaction. The nascent protein contains a N-terminal signal peptide sequence, a conserved "ZP domain" module, a consensus furin cleavage site (CFCS), a polymerization-blocking external hydrophobic patch (EHP), and a C-terminal transmembrane domain. Cleavage at the CFCS separates the mature protein from the EHP, allowing it to incorporate into nascent ZP filaments. A variation in the last exon of this gene has previously served as the basis for an additional ZP3 locus; however, sequence and literature review reveals that there is only one full-length ZP3 locus in the human genome. Another locus encoding a bipartite transcript designated POMZP3 contains a duplication of the last four exons of ZP3, including the above described variation, and maps closely to this gene. [5]
In mice, ZP3 (more specifically the portion in its exon 7) is the single ZP protein that is sufficient and necessary for sperm binding in vitro, [6] but is insufficient for fertilization in vivo. [7] In humans, ZP1, ZP3, and ZP4 all appear partially responsible for starting the acrosome reaction. [8]
Orthologs of these genes are found throughout Vertebrata. The western clawed frog appears to have two orthologs, and the sea lamprey has seven. [9]
3D Structure
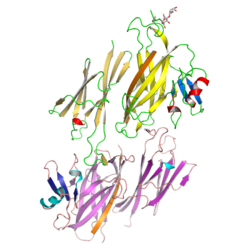
X-ray crystallographic studies of the N-terminal half of mammalian ZP3 ( PDB: 3D4C, 3D4G, 3EF7, 5OSQ ) [10] as well as its full-length avian homolog ( PDB: 3NK3, 3NK4 ) [11] revealed that the protein's ZP module consists of two immunoglobulin-like domains, ZP-N and ZP-C. The latter, which contains EHP as well as a ZP3-specific subdomain, interacts with the ZP-N domain of a second molecule to generate an antiparallel homodimeric arrangement required for protein secretion. [11]
Mutations
The Zona Pellucida (ZP) is a complex matrix of glycoprotein that surrounds the oocyte and plays a crucial role in the attachment of sperm during reproduction. Ultimately, through the facilitation of sperm binding and the initiation of the acrosome reaction, the ZP proteins are essential to reproduction and have an important impact on fertility. Research through the Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine conducted experiments to determine the mechanisms surrounding possible mutations to the ZP gene and how they would impact fertility. [12] By performing whole-exome sequencing they isolated a genome that had a mutation in the ZP3 and the ZP1 genes. They then transfected these genes into HeLa cell cultures and ran a variety of tests to isolate the consequences of these mutations. The authors wrote this regarding their results:
“The results indicate that the mutations are involved in the reduced secretion of ZP1 and ZP3 and leading to connection failure of the ZP filaments in vitro. The data suggest a potential that the mutations may be involved in the lacking ZP phenotype, which need to be further investigated in vivo.” (Cao, Qiqi, et al.)
It is clear that the ZP proteins are crucial to expressing a correct ZP phenotype in humans, in which all of the ZP proteins 1-4 are properly functioning. Without this interface of proper protein function, sperm binding is inhibited, and fertility is compromised.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.