Related Research Articles

The ulna or ulnar bone is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the radius, the forearm's other long bone. Longer and thinner than the radius, the ulna is considered to be the smaller long bone of the lower arm. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. The radius is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.

The lesser omentum is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into these two connecting parts: the hepatogastric ligament, and the hepatoduodenal ligament.
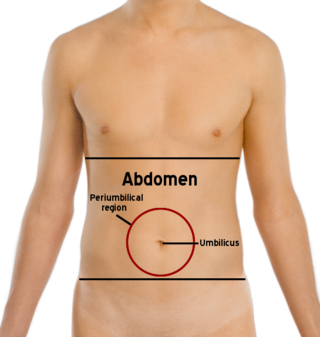
The abdomen is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax.

The lesser sac, also known as the omental bursa, is a part of the peritoneal cavity that is formed by the lesser and greater omentum. Usually found in mammals, it is connected with the greater sac via the omental foramen or Foramen of Winslow. In mammals, it is common for the lesser sac to contain considerable amounts of fat.

The ischium forms the lower and back region of the hip bone.

In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body.

In human anatomy, the falciform ligament is a ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall and divides the liver into the left lobe and right lobe. The falciform ligament is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being directed downward and backward and its apex upward and forward. It droops down from the hilum of the liver.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone, positioned in the skull behind each eye. There is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.

The lateral parts of the occipital bone are situated at the sides of the foramen magnum; on their under surfaces are the condyles for articulation with the superior facets of the atlas.

The greater omentum is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum, which hangs down from the liver to the lesser curvature. The common anatomical term "epiploic" derives from "epiploon", from the Greek epipleein, meaning to float or sail on, since the greater omentum appears to float on the surface of the intestines. It is the first structure observed when the abdominal cavity is opened anteriorly.
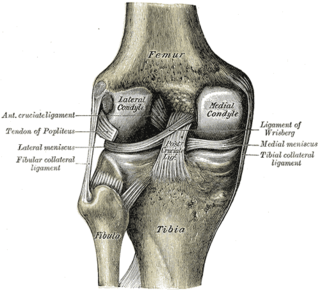
The lower extremity of femur is the lower end of the femur in human and other animals, closer to the knee. It is larger than the upper extremity of femur, is somewhat cuboid in form, but its transverse diameter is greater than its antero-posterior; it consists of two oblong eminences known as the lateral condyle and medial condyle.

The coronary ligament of the liver refers to parts of the peritoneal reflections that hold the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm.
The paracolic gutters are peritoneal recesses – spaces between the colon and the abdominal wall.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
The development of the digestive system in the human embryo concerns the epithelium of the digestive system and the parenchyma of its derivatives, which originate from the endoderm. Connective tissue, muscular components, and peritoneal components originate in the mesoderm. Different regions of the gut tube such as the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, etc. are specified by a retinoic acid gradient that causes transcription factors unique to each region to be expressed. Differentiation of the gut and its derivatives depends upon reciprocal interactions between the gut endoderm and its surrounding mesoderm. Hox genes in the mesoderm are induced by a Hedgehog signaling pathway secreted by gut endoderm and regulate the craniocaudal organization of the gut and its derivatives. The gut system extends from the oropharyngeal membrane to the cloacal membrane and is divided into the foregut, midgut, and hindgut.

The human abdomen is divided into quadrants and regions by anatomists and physicians for the purposes of study, diagnosis, and treatment. The division into four quadrants allows the localisation of pain and tenderness, scars, lumps, and other items of interest, narrowing in on which organs and tissues may be involved. The quadrants are referred to as the left lower quadrant, left upper quadrant, right upper quadrant and right lower quadrant. These terms are not used in comparative anatomy, since most other animals do not stand erect.

In human anatomy, the liver is divided grossly into four parts or lobes: the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe. Seen from the front – the diaphragmatic surface – the liver is divided into two lobes: the right lobe and the left lobe. Viewed from the underside – the visceral surface – the other two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are also visible. The two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are known as superficial or accessory lobes, and both are located on the underside of the right lobe.
References
- ↑ Pérez, W; Lima, M (March 2007). "Anatomical Description of the Liver, Hepatic Ligaments and Omenta in the Coypu (Myocastor coypus)". International Journal of Morphology. 25 (1). doi: 10.4067/S0717-95022007000100007 . ISSN 0717-9502.
- ↑ Anatomy photo:38:10-0204 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Ligaments of the Liver"