The cecum or caecum is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body. The word cecum stems from the Latin caecus meaning blind.

The ileum is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum.
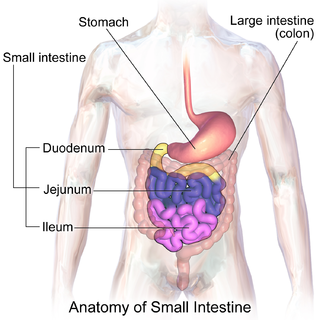
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about 18 feet long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter.

The appendix is a finger-like, blind-ended tube connected to the cecum, from which it develops in the embryo. The cecum is a pouch-like structure of the large intestine, located at the junction of the small and the large intestines. The term "vermiform" comes from Latin and means "worm-shaped." The appendix used to be considered a vestigial organ, but this view has changed over the past decades. Research suggests that the appendix may serve an important purpose. In particular, it may serve as a reservoir for beneficial gut bacteria.

The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions.

In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the ascending colon is the part of the colon located between the cecum and the transverse colon.
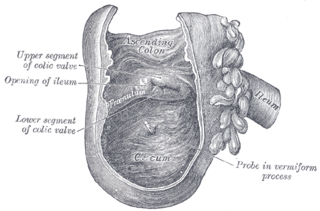
The ileocecal valve is a sphincter muscle valve that separates the small intestine and the large intestine. Its critical function is to limit the reflux of colonic contents into the ileum. Approximately two liters of fluid enters the colon daily through the ileocecal valve.

The ileocolic artery is the lowest branch arising from the concavity of the superior mesenteric artery.
In many Animalia, including humans, an ileocolic structure or problem is something that concerns the region of the gastrointestinal tract from the ileum to the colon. In Animalia that have ceca, the ileocecal region is a subset of the ileocolic region, and the entire range can also be described as ileocecocolic, whereas in some Animalia, the ileocolic region contains no cecum, as the ileum joins the colon directly.

The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and the small wings and front part of the body of the sphenoid; it is limited behind by the posterior borders of the small wings of the sphenoid and by the anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove. The lesser wings of the sphenoid separate the anterior and middle fossae.
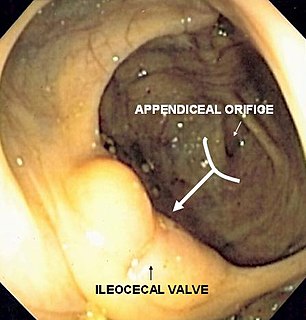
The bow and arrow sign is an endoscopic sign for determining the location of the ileocecal valve during colonoscopy. Identifying the ileocecal valve in a colonoscopy is important, as it indicates that the entire colon has been visualized.
The paracolic gutters are peritoneal recesses – spaces between the colon and the abdominal wall.
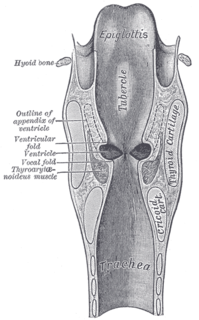
The laryngeal ventricle, is a fusiform fossa, situated between the vestibular and vocal folds on either side, and extending nearly their entire length. There is also a sinus of Morgagni in the pharynx.
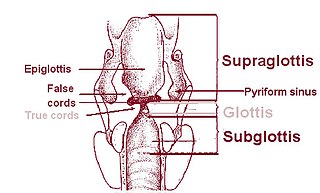
On either side of the laryngeal orifice in humans is a recess, termed the pyriform sinus, which is bounded medially by the aryepiglottic fold, laterally by the thyroid cartilage and thyrohyoid membrane. The fossae are involved in speech.

Skin folds or skinfolds are areas of skin that are naturally folded. Many skin folds are distinct, heritable anatomical features, and may be used for identification of animal species, while others are non-specific and may be produced either by individual development of an organism or by arbitrary application of force to skin, either by the actions of the muscles of the body or by external force, e.g., gravity. Anatomical folds can also be found in other structures and tissues besides the skin, such as the ileocecal fold beneath the terminal ileum of the cecum.

The abdominopelvic cavity is a body cavity that consists of the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. The upper portion is the abdominal cavity, and it contains the stomach, liver, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, small intestine, and most of the large intestine. The lower portion is the pelvic cavity, and it contains the urinary bladder, the rest of the large intestine, and the internal reproductive organs.

The superior mesenteric lymph nodes may be divided into three principal groups:

Sir Frederick Treves, 1st Baronet was a prominent British surgeon, and an expert in anatomy. Treves was renowned for his surgical treatment of appendicitis, and is credited with saving the life of King Edward VII in 1902. He is also widely known for his friendship with Joseph Merrick, dubbed the "Elephant Man" for his severe deformities.
Cecal bascule is a cause of large bowel obstruction where there is folding of the cecum anteriorly over the ascending colon. It is one of two types of cecal volvulus, the other being axial ileocolic. It is caused by rotational torsion of the cecum or ascending colon along its own axis. In cecal bascule, the base of the cecum folds anteriorly over the ascending colon, creating a flap-valve, obstructing emptying of the cecum. The condition can be complicated by necrosis or organ perforation before the diagnosis is made, particularly if the ileocecal valve is competent, preventing retrograde decompression of the cecum into the ileum.