Related Research Articles
Environmental finance is a field within finance that employs market-based environmental policy instruments to improve the ecological impact of investment strategies. The primary objective of environmental finance is to regress the negative impacts of climate change through pricing and trading schemes. The field of environmental finance was established in response to the poor management of economic crises by government bodies globally. Environmental finance aims to reallocate a businesses resources to improve the sustainability of investments whilst also retaining profit margins.
The United Kingdom's Climate Change Programme was launched in November 2000 by the British government in response to its commitment agreed at the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED). The 2000 programme was updated in March 2006 following a review launched in September 2004.

Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include conserving energy and replacing fossil fuels with clean energy sources. Secondary mitigation strategies include changes to land use and removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Current climate change mitigation policies are insufficient as they would still result in global warming of about 2.7 °C by 2100, significantly above the 2015 Paris Agreement's goal of limiting global warming to below 2 °C.
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI, pronounced "Reggie") is the first mandatory market-based program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States. RGGI is a cooperative effort among the states of Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia to cap and reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the power sector. RGGI compliance obligations apply to fossil-fueled power plants 25 megawatts (MW) and larger within the 11-state region. Pennsylvania's participation in the RGGI cooperative was ruled unconstitutional on November 1, 2023, although that decision has been appealed. North Carolina's entrance into RGGI has been blocked by the enactment of the state's fiscal year 2023–25 budget.
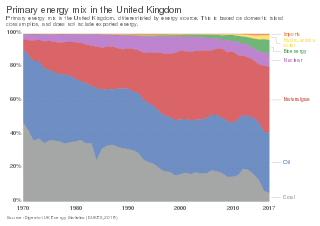
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.
The Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006, or Assembly Bill (AB) 32, is a California state law that fights global warming by establishing a comprehensive program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from all sources throughout the state. AB32 was co-authored by Assemblymember Fran Pavley and Speaker of the California Assembly Fabian Nunez and signed into law by Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger on September 27, 2006.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.

A green-collar worker is a worker who is employed in an environmental sector of the economy. Environmental green-collar workers satisfy the demand for green development. Generally, they implement environmentally conscious design, policy, and technology to improve conservation and sustainability. Formal environmental regulations as well as informal social expectations are pushing many firms to seek professionals with expertise with environmental, energy efficiency, and clean renewable energy issues. They often seek to make their output more sustainable, and thus more favorable to public opinion, governmental regulation, and the Earth's ecology.

The Global Warming Pollution Reduction Act of 2007 (S. 309) was a bill proposed to amend the 1963 Clean Air Act, a bill that aimed to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2). U.S. Senator, Bernie Sanders (I-VT), introduced the resolution in the 110th United States Congress on January 16, 2007. The bill was referred to the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works but was not enacted into law.
The environmental policy of the United States is a federal governmental action to regulate activities that have an environmental impact in the United States. The goal of environmental policy is to protect the environment for future generations while interfering as little as possible with the efficiency of commerce or the liberty of the people and to limit inequity in who is burdened with environmental costs. As his first official act bringing in the 1970s, President Richard Nixon signed the U.S. National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) into law on New Years Day, 1970. Also in the same year, America began celebrating Earth Day, which has been called "the big bang of U.S. environmental politics, launching the country on a sweeping social learning curve about ecological management never before experienced or attempted in any other nation." NEPA established a comprehensive US national environmental policy and created the requirement to prepare an environmental impact statement for "major federal actions significantly affecting the quality of the environment." Author and consultant Charles H. Eccleston has called NEPA the world's "environmental Magna Carta".
New Energy for America was a plan led by Barack Obama and Joe Biden beginning in 2008 to invest in renewable energy sources, reduce reliance on foreign oil, address global warming issues, and create jobs for Americans. The main objective of the New Energy for America plan was to implement clean energy sources in the United States to switch from nonrenewable resources to renewable resources. The plan led by the Obama Administration aimed to implement short-term solutions to provide immediate relief from pain at the pump, and mid- to- long-term solutions to provide a New Energy for America plan. The goals of the clean energy plan hoped to: invest in renewable technologies that will boost domestic manufacturing and increase homegrown energy, invest in training for workers of clean technologies, strengthen the middle class, and help the economy.

The Clean Air Act (CAA) is the United States' primary federal air quality law, intended to reduce and control air pollution nationwide. Initially enacted in 1963 and amended many times since, it is one of the United States' first and most influential modern environmental laws.

The American Clean Energy and Security Act of 2009 (ACES) was an energy bill in the 111th United States Congress that would have established a variant of an emissions trading plan similar to the European Union Emission Trading Scheme. The bill was approved by the House of Representatives on June 26, 2009, by a vote of 219–212. With no prospect of overcoming a threatened Republican filibuster, the bill was never brought to the floor of the Senate for discussion or a vote. The House passage of the bill was the "first time either house of Congress had approved a bill meant to curb the heat-trapping gases scientists have linked to climate change."
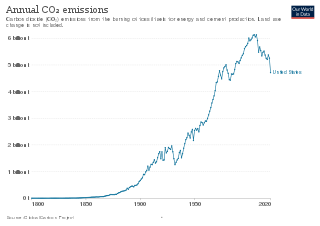
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. Cumulatively, the United States has emitted over a trillion metric tons of greenhouse gases, more than any country in the world.
The Sustainable Communities and Climate Protection Act of 2008, also known as Senate Bill 375 or SB 375, is a State of California law targeting greenhouse gas emissions from passenger vehicles. The Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006 sets goals for the reduction of statewide greenhouse gas emissions. Passenger vehicles are the single largest source of greenhouse gas emissions statewide, accounting for 30% of total emissions. SB 375 therefore provides key support to achieve the goals of AB 32.

The Clean Power Plan was an Obama administration policy aimed at combating climate change that was first proposed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in June 2014. The final version of the plan was unveiled by President Barack Obama on August 3, 2015. Each state was assigned an individual goal for reducing carbon emissions, which could be accomplished how they saw fit, but with the possibility of the EPA stepping in if the state refused to submit a plan. If every state met its target, the plan was projected to reduce carbon emissions from electricity generation 32% by 2030, relative to 2005 levels, as well as achieving various health benefits due to reduced air pollution.

As the most populous state in the United States, California's climate policies influence both global climate change and federal climate policy. In line with the views of climate scientists, the state of California has progressively passed emission-reduction legislation.
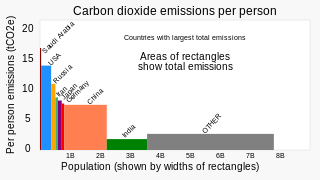
China's greenhouse gas emissions are the largest of any country in the world both in production and consumption terms, and stem mainly from coal burning, including coal power, coal mining, and blast furnaces producing iron and steel. When measuring production-based emissions, China emitted over 14 gigatonnes (Gt) CO2eq of greenhouse gases in 2019, 27% of the world total. When measuring in consumption-based terms, which adds emissions associated with imported goods and extracts those associated with exported goods, China accounts for 13 gigatonnes (Gt) or 25% of global emissions. According to the Carbon Majors Database, Chinese state coal production alone accounts for 14% of historic global emissions.
The environmental policy of the Joe Biden administration includes a series of laws, regulations, and programs introduced by United States President Joe Biden since he took office in January 2021. Many of the actions taken by the Biden administration reversed the policies of his predecessor, Donald Trump. Biden's climate change policy focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, similar to the efforts taken by the Obama administration. Biden promised to end and reverse deforestation and land degradation by 2030. The main climate target of the Biden administration is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States to net zero by 2050. A climate team was created to lead the effort.
West Virginia v. Environmental Protection Agency, 597 U.S. 697 (2022), is a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court relating to the Clean Air Act, and the extent to which the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) can regulate carbon dioxide emissions related to climate change.
References
- ↑ "NY State Senate Bill S6599". NY State Senate. June 18, 2019. Retrieved May 20, 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 June 20; Alum, 2019 Jackson Morris Miles Farmer-. "Unpacking New York's Big New Climate Bill: A Primer". NRDC. Retrieved May 20, 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - 1 2 3 4 McKinley, Jesse; Plumer, Brad (June 18, 2019). "New York to Approve One of the World's Most Ambitious Climate Plans". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331 . Retrieved May 20, 2020.
- ↑ Carlson, Ann; Professor, Environmental Law; California, University of; Angeles, Los. "Trump Administration Weakens Auto Emissions Standards". NPR.org. Retrieved May 20, 2020.
- ↑ "Trump Administration Challenges California And Automakers On Fuel Economy". NPR.org. Retrieved May 20, 2020.
- ↑ "'Gridlock' Gov's Congestion Pricing Retreat May Trigger Pro-Toll Lawsuits - Streetsblog New York City". nyc.streetsblog.org. June 7, 2024. Retrieved June 26, 2024.
- ↑ "NY Renews". NY Renews. Retrieved May 20, 2020.
- ↑ French, Marie J.; Rivard, Ry. "NY Renews launches new campaign". POLITICO. Retrieved March 26, 2023.