The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere. It was signed by 154 states at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), informally known as the Earth Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro from 3 to 14 June 1992. It established a Secretariat headquartered in Bonn, Germany, and entered into force on 21 March 1994.

The Climatic Research Unit (CRU) is a component of the University of East Anglia and is one of the leading institutions concerned with the study of natural and anthropogenic climate change.
Real estate appraisal, property valuation or land valuation is the process of developing an opinion of value for real property. Real estate transactions often require appraisals because they occur infrequently and every property is unique, unlike corporate stocks, which are traded daily and are identical. The location also plays a key role in valuation. However, since property cannot change location, it is often the upgrades or improvements to the home that can change its value. Appraisal reports form the basis for mortgage loans, settling estates and divorces, taxation, and so on. Sometimes an appraisal report is used to establish a sale price for a property.

In animal husbandry, a concentrated animal feeding operation (CAFO), as defined by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), is an intensive animal feeding operation (AFO) in which over 1,000 animal units are confined for over 45 days a year. An animal unit is the equivalent of 1,000 pounds of "live" animal weight. A thousand animal units equates to 700 dairy cows, 1,000 meat cows, 2,500 pigs weighing more than 55 pounds (25 kg), 10,000 pigs weighing under 55 pounds, 10,000 sheep, 55,000 turkeys, 125,000 chickens, or 82,000 egg laying hens or pullets.
Climate change mitigation consists of actions to limit global warming. The recent rise in temperature is mostly caused by the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide CO2 which is released when burning coal, oil, and gas for energy use. This can be reduced by a transition from these fossil fuels to other sources, energy conservation and efficiency. CO2 can be removed from the atmosphere by enlarging forests and other natural and technical processes.

The economics of climate change concerns the economic aspects of climate change; this can inform policies that governments might consider in response. A number of factors make this and the politics of climate change a difficult problem: it is a long-term, intergenerational problem; benefits and costs are distributed unequally both within and across countries; and both the scientific consensus and public opinion on climate change need to be taken into account.

Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to current or expected effects of climate change. It is one of the ways to respond to climate change, along with mitigation. For humans, adaptation aims to moderate or avoid harm, and exploit opportunities; for natural systems, humans may intervene to help adjustment. Adaptation actions can be either incremental or transformative. The need for adaptation varies from place to place, depending on the risk to human or ecological systems.
The Climate Change Science Program (CCSP) was the program responsible for coordinating and integrating research on global warming by U.S. government agencies from February 2002 to June 2009. Toward the end of that period, CCSP issued 21 separate climate assessment reports that addressed climate observations, changes in the atmosphere, expected climate change, impacts and adaptation, and risk management issues. Shortly after President Obama took office, the program's name was changed to U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) which was also the program's name before 2002. Nevertheless, the Obama Administration generally embraced the CCSP products as sound science providing a basis for climate policy. Because those reports were mostly issued after the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), and in some cases focused specifically on the United States, they were generally viewed within the United States as having an importance and scientific credibility comparable to the IPCC assessments for the first few years of the Obama Administration.

In the United States, an environmental site assessment is a report prepared for a real estate holding that identifies potential or existing environmental contamination liabilities. The analysis, often called an ESA, typically addresses both the underlying land as well as physical improvements to the property. A proportion of contaminated sites are "brownfield sites." In severe cases, brownfield sites may be added to the National Priorities List where they will be subject to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's Superfund program.
A Comp Check is a request made to a State Licensed or Certified real estate appraiser, sometimes to assure a minimum opinion of value before an order, is placed. Because providing an opinion of value is the definition of an appraisal in the United States, the practice of the look-up, when excess care is not taken, runs a greater risk of being in violation of the Uniform Standards of Professional Appraisal Practice (USPAP) than an assignment with a more thorough Scope of Work.
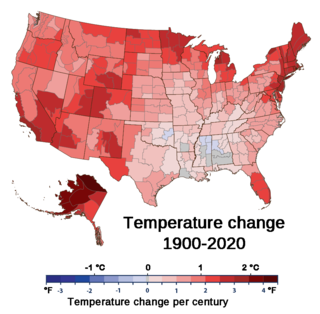
Climate change in the United States has led to the country warming by 2.6 °F since 1970. Due to climate change, the climate of the United States is shifting in ways that are widespread and varied between regions. From 2010 to 2019, the United States experienced its hottest decade on record. Extreme weather events, invasive species, floods and droughts are increasing. Climate change's impacts on tropical cyclones and sea level rise also affects regions of the country.

The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and on global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. In total the United States has emitted over 400 billion metric tons of greenhouse gasses, more than any country in the world.

Climate change and poverty are deeply intertwined because climate change disproportionally affects poor people in low-income communities and developing countries around the world. Those in poverty have a higher chance of experiencing the ill-effects of climate change due to the increased exposure and vulnerability. Vulnerability represents the degree to which a system is susceptible to, or unable to cope with, adverse effects of climate change including climate variability and extremes.
Territorialisation of Carbon Governance (ToCG) is a concept used in political geography or environmental policy which is considered to be a new logic of environmental governance. This method creates carbon-relevant citizens who become enrolled in the process of governing the climate. The territorialisation of carbon governance transforms climate change from a global to local issue. It embodies political practices that serve to connect the causes and consequences of global climate change to local communities.
The NOAA National Operational Model Archive and Distribution System (NOMADS) is a Web-services based project providing both real-time and retrospective format independent access to climate and weather model data.
Real estate is property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as crops, minerals or water; immovable property of this nature; an interest vested in this (also) an item of real property, buildings or housing in general. In terms of law, real is in relation to land property and is different from personal property while estate means the "interest" a person has in that land property.

Coastal Risk Consulting, LLC. is an American startup climate adaptation technology and consulting company with headquarters in Plantation, Florida. Coastal Risk provides individuals, businesses, and local governments with climate impact modeling technology, available as an online software-as-a-service (SaaS), that allows property owners to assess their vulnerability to flooding related to sea level rise and climate change impacts and assists in adaptation and resiliency decision-making.

Climate change art is art inspired by climate change and global warming, generally intended to overcome humans' hardwired tendency to value personal experience over data and to disengage from data-based representations by making the data "vivid and accessible". One of the goal of climate change art is to "raise awareness of the crisis", as well as engage viewers politically and environmentally.

Climate communication or climate change communication is a field of environmental communication and science communication focused on the causes, nature and effects of anthropogenic climate change.










