Related Research Articles

In amniotes, the clitoris is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female sexual pleasure. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 nerve endings.

Orgasm or sexual climax is the sudden release of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, characterized by intense sexual pleasure resulting in rhythmic, involuntary muscular contractions in the pelvic region. Orgasms are controlled by the involuntary or autonomic nervous system and experienced by both males and females; the body's response includes muscular spasms, a general euphoric sensation, and, frequently, body movements and vocalizations. The period after orgasm is typically a relaxing experience, after the release of the neurohormones oxytocin and prolactin, as well as endorphins.

The G-spot, also called the Gräfenberg spot, is characterized as an erogenous area of the vagina that, when stimulated, may lead to strong sexual arousal, powerful orgasms and potential female ejaculation. It is typically reported to be located 5–8 cm (2–3 in) up the front (anterior) vaginal wall between the vaginal opening and the urethra and is a sensitive area that may be part of the female prostate.

A clitoral hood piercing is a female genital piercing through the clitoral hood surrounding the clitoris. In addition to being an adornment, a clitoral hood piercing can enhance sexual pleasure during masturbation, foreplay and intercourse. In an empirical study at the University of South Alabama, the authors reported a positive relationship between vertical clitoral hood piercings and desire, frequency of intercourse, and sexual arousal. There are two main types of clitoral hood piercing: the vertical clitoral hood (VCH) piercing and the horizontal clitoral hood (HCH) piercing. As the names indicate, the difference is in the direction the piercing is oriented in the skin above the clitoris. Neither of these piercings penetrates the clitoris itself, although in common parlance they are sometimes called "clit" piercings. The deep hood piercing is a variation of the clitoral hood piercing that passes deeper through the clitoral hood.
Anorgasmia is a type of sexual dysfunction in which a person cannot achieve orgasm despite adequate sexual stimulation. Anorgasmia is far more common in females than in males and is especially rare in younger men. The problem is greater in women who are post-menopausal. In males, it is most closely associated with delayed ejaculation. Anorgasmia can often cause sexual frustration.

Sexual stimulation is anything that leads to sexual arousal or orgasm. This thing can be physical or of other senses, and is known as a stimulus.
Penile plethysmography (PPG) or phallometry is a measurement of blood flow to the penis, typically used as a proxy for measurement of sexual arousal. The most commonly reported methods of conducting penile plethysmography involves the measurement of the circumference of the penis with a mercury-in-rubber or electromechanical strain gauge, or the volume of the penis with an airtight cylinder and inflatable cuff at the base of the penis. Corpora cavernosa nerve penile plethysmographs measure changes in response to inter-operative electric stimulation during surgery. The volumetric procedure was invented by Kurt Freund and is considered to be particularly sensitive at low arousal levels. The easier to use circumferential measures are more widely used, however, and more common in studies using erotic film stimuli. A corresponding device in women is the vaginal photoplethysmograph.

A plethysmograph is an instrument for measuring changes in volume within an organ or whole body. The word is derived from the Greek "plethysmos", and "graphein".
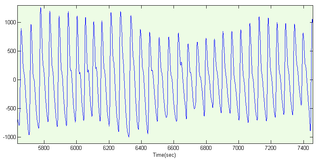
A photoplethysmogram (PPG) is an optically obtained plethysmogram that can be used to detect blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue. A PPG is often obtained by using a pulse oximeter which illuminates the skin and measures changes in light absorption. A conventional pulse oximeter monitors the perfusion of blood to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin.
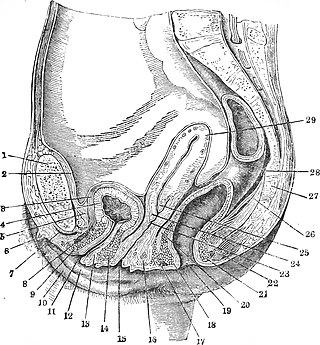
The urethral sponge is a spongy cushion of tissue, found in the lower genital area of females, that sits against both the pubic bone and vaginal wall, and surrounds the urethra.
Vaginal photoplethysmography is a technique using light to measure the amount of blood in the walls of the vagina. The device that is used is called a vaginal photometer.

The labia are the major externally visible structures of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the labia majora are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts, while the labia minora are the folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the urethral and vaginal openings, as well as the glans clitoris.

Sexual activities involving women who have sex with women (WSW), regardless of their sexual orientation or sexual identity, can include oral sex, manual sex, or tribadism. Sex toys may be used.

Human female sexuality encompasses a broad range of behaviors and processes, including female sexual identity and sexual behavior, the physiological, psychological, social, cultural, political, and spiritual or religious aspects of sexual activity. Various aspects and dimensions of female sexuality, as a part of human sexuality, have also been addressed by principles of ethics, morality, and theology. In almost any historical era and culture, the arts, including literary and visual arts, as well as popular culture, present a substantial portion of a given society's views on human sexuality, which includes both implicit (covert) and explicit (overt) aspects and manifestations of feminine sexuality and behavior.

Clitoral hood reduction, also termed clitoral hoodectomy, clitoral unhooding, clitoridotomy, or (partial) hoodectomy, is a plastic surgery procedure for reducing the size and the area of the clitoral hood in order to further expose the glans of the clitoris.
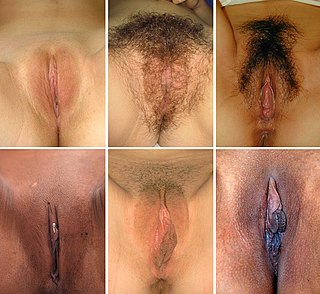
In mammals, the vulva comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female genitalia leading away from the interior parts of the female reproductive tract, starting at the vaginal opening. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands. The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support.

Sexual arousal describes the physiological and psychological responses in preparation for sexual intercourse or when exposed to sexual stimuli. A number of physiological responses occur in the body and mind as preparation for sexual intercourse, and continue during intercourse. Male arousal will lead to an erection, and in female arousal, the body's response is engorged sexual tissues such as nipples, clitoris, vaginal walls, and vaginal lubrication.
The labial thermistor clip is a device used measure the skin temperature of the labia minora and is associated blood engorgement. This device consists of a thermistor affixed to a small metal clip that can be attached to the labia minora. The labial thermistor clip is the second most commonly used physiological measure of female genital response, next to the vaginal photoplethysmograph (VPG). Both devices can be used simultaneously. The labial thermistor clip has some advantages over VPG, including better test-retest reliability, greater correlation between genital and self-reported sexual arousal, and an absolute unit of change (temperature). Like VPG, the labial thermistor clip has discriminant validity; that is, it detects differences between sexual and nonsexual stimuli. It is also sensitive to different levels of sexual arousal. The labial thermistor clip has some disadvantages because participants have difficulty with placing the device correctly and some report discomfort with using the device.

Laser Doppler imaging (LDI) is an imaging method that uses a laser beam to image live tissue. When the laser light reaches the tissue, the moving blood cells generate Doppler components in the reflected (backscattered) light. The light that comes back is detected using a photodiode that converts it into an electrical signal. Then the signal is processed to calculate a signal that is proportional to the tissue perfusion in the imaged area. When the process is completed, the signal is processed to generate an image that shows the perfusion on a screen.
Sexual concordance refers to the degree of correlation between subjective sexual arousal and physiological genital response. This phenomenon is often studied within the fields of sexology and psychology to understand the complex relationship between the mind and body during sexual activity.
References
- ↑ Gerritsen, J., van der Made, F., Bloemers, J., van Ham, D., Kleiverda, G., Everaerd, W., et al. ["The clitoral photoplethysmograph: A new way of assessing genital arousal in women"], "Journal of Sexual Medicine, 6, 1678 – 1687", 2009
- ↑ Schlank, Anita, Saprina Matheny, and Jessica Schilling. "Overview of Assessment of Sexual Offenders." Sexual Offending. Springer New York, 2016. 247-264