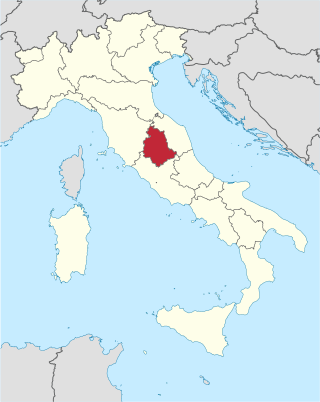
Umbria is a region of central Italy. It includes Lake Trasimeno and Marmore Falls, and is crossed by the River Tiber. It is the only landlocked region on the Apennine Peninsula. The regional capital is Perugia.

Spoleto is an ancient city in the Italian province of Perugia in east-central Umbria on a foothill of the Apennines. It is 20 km (12 mi) S. of Trevi, 29 km (18 mi) N. of Terni, 63 km (39 mi) SE of Perugia; 212 km (132 mi) SE of Florence; and 126 km (78 mi) N of Rome.

Todi is a town and comune (municipality) of the province of Perugia in central Italy. It is perched on a tall two-crested hill overlooking the east bank of the river Tiber, commanding distant views in every direction.

Bevagna is a town and comune in the central part of the Italian province of Perugia (Umbria), in the flood plain of the Topino river.

Narni is an ancient hilltown and comune of Umbria, in central Italy, with 19,252 inhabitants (2017). At an altitude of 240 m (787 ft), it overhangs a narrow gorge of the Nera River in the province of Terni. It is very close to the geographic center of Italy. There is a stone on the exact spot with a sign in multiple languages.
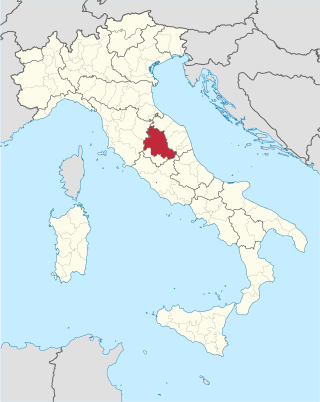
The Province of Perugia is the larger of the two provinces in the Umbria region of Italy, comprising two-thirds of both the area and population of the region. Its capital is the city of Perugia. The province covered all of Umbria until 1927, when the province of Terni was carved out of its southern third. The province of Perugia has an area of 6,334 km² covering two-thirds of Umbria, and a total population of about 660,000. There are 59 comunes in the province. The province has numerous tourist attractions, especially artistic and historical ones, and is home to the Lake Trasimeno, the largest lake of Central Italy. It is historically the ancestral origin of the Umbri, while later it was a Roman province and then part of the Papal States until the late 19th century.

Trevi is an ancient town and comune in Umbria, Italy, on the lower flank of Monte Serano overlooking the wide plain of the Clitunno river system. It is 10 km (6 mi) SSE of Foligno and 20 km (12 mi) north of Spoleto.

Foligno is an ancient town of Italy in the province of Perugia in east central Umbria, on the Topino river where it leaves the Apennines and enters the wide plain of the Clitunno river system. It is located 40 kilometres south-east of Perugia, 10 km (6 mi) north-north-west of Trevi and 6 km (4 mi) south of Spello.

Spello is an ancient town and comune (township) of Italy, in the province of Perugia in eastern-central Umbria, on the lower southern flank of Mt. Subasio. It is 6 km (4 mi) NNW of Foligno and 10 km (6 mi) SSE of Assisi.
Cannaiola is a village of 730 inhabitants in the Italian province of Perugia in east central Umbria in the floodplain of the Clitunno River; altitude 218 m (715 ft) above sea-level. It is a frazione of the comune of Trevi, which lies 3.5 km to the east.

Pigge or Lapigge is a village in the Italian province of Perugia in east central Umbria, stretching from the plain of the Clitunno river up the lower SW flank of Mt. Serano, at 297 m above sea-level. It is a frazione of the comune of Trevi, which is 3 km NNW. Its population was 463 in 2003.

Hispellum was an ancient town of Umbria, Italy, 6 km (3.7 mi) north of Fulginiae, on the road between it and Perusia.

Regio VI Umbria is the name for one of the 11 administrative regions into which the emperor Augustus divided Italy. The main source for the regions is the Historia Naturalis of Pliny the Elder, who informs his readers he is basing the geography of Italy on the descriptio Italiae, "division of Italy," made by Augustus. The Regio Sexta is called Umbria complexa agrumque Gallicam citra Ariminium, "Umbria including the Gallic country this side of Rimini."
The Umbri were an Italic people of ancient Italy. A region called Umbria still exists and is now occupied by Italian speakers. It is somewhat smaller than the ancient Umbria.

Nocera Umbra is a town and comune in the province of Perugia, Italy, 15 kilometers north of Foligno, at an altitude of 520 m above sea-level. The comune, covering an area of 157.19 km², is one of the largest in Umbria.

Amelia is a town and comune of the province of Terni, in the Umbria region of central Italy. It grew up around an ancient hill fort, known to the Romans as Ameria.

Barbarian Odes is a collection of three books of poetry by Giosuè Carducci, published between 1877 and 1889.
The Fanum Voltumnae was the chief sanctuary of the Etruscans; fanum means a sacred place, a much broader notion than a single temple. Numerous sources refer to a league of the "Twelve Peoples" (lucumonies) of Etruria, formed for religious purposes but evidently having some political functions. The Etruscan league of twelve city-states met annually at the Fanum, located in a place chosen as omphalos, the geographical and spiritual centre of the whole Etruscan nation. Each spring political and religious leaders from the cities would meet to discuss military campaigns and civic affairs and pray to their common gods. Chief amongst these was Voltumna, possibly state god of the Etruria.

The Galleria Nazionale dell'Umbria the Italian national paintings collection of Umbria, housed in the Palazzo dei Priori, Perugia, in central Italy. Located on the upper floors of the Palazzo dei Priori, the exhibition spaces occupy two floors and the collection comprises the greatest representation of the Umbrian School of painting, ranging from the 13th to the 19th century, strongest in the fourteenth through sixteenth centuries. The collection is presented in 40 exhibition rooms in the Palazzo. On the second floor of the Gallery, there is an exhibition space for temporary collections, changed several times a year.

The so-called Temple of Clitumnus is a small early medieval church that sits along the banks of the Clitunno river in the town of Pissignano near Campello sul Clitunno, Umbria]], Italy. In 2011, it became a UNESCO World Heritage Site as part of a group of seven such sites that mark the presence of Longobards in Italy: Places of Power.



















